By Debbie Burke
@burke_writer
After lunch on the second day of a writing conference, typically attendees’ brains are already brimming. Fatigue sets in. With full tummies, the temptation to nod off is strong.

Editor Val Mathews
However, no one dozed during Val Mathews’s presentation at the Flathead River Writers Conference in Montana this past October.
Val is a former acquisitions editor at The Wild Rose Press and teaches at several universities. She’s a certified flight instructor and used to fly Lear jets. Additionally, she’s a gifted speaker who knows how to grab and keep an audience’s attention.
At the beginning of her talk, Val got about 100 attendees up on our feet and walking between long rows of tables and down the aisles of the auditorium. Initially, she asked us to imagine we were taking a leisurely hike in Glacier Park. What did we see, smell, and hear?
Then she switched the scenario to a crowded city street. We were late to an important meeting, had forgotten our notes, and needed to return to the office to retrieve them. The energy in the room increased. The sea of people hurried around, now moving in opposite directions, passing each other and trying to avoid collisions.
Next, Val reduced the pace and had us walk with different postures—chests out, heads lowered, hunched over, hips forward, speeding up, slowing down—while paying attention to how each variation made our bodies feel.
Then she told us to become our main character and emulate their posture, movements, stride, and attitude. She asked, “How does your character feel? What are the physical sensations? What are they thinking about? How does that affect their movement?”
After ten minutes, Val had succeeded in chasing away all drowsiness and captured our full attention.
The exercise impressed me, so I invited Val to visit The Kill Zone. Welcome, Val!
Debbie Burke: Please share a little of your background and how you ended up in the publishing business.
Val Mathews: Thanks for having me, Debbie. I’m so glad you enjoyed my workshops! They are always so much fun to do, and everyone comes away renewed with ideas and inspired to write!
By the way, that opening exercise was borrowed from acting classes I took recently. Acting is all about stepping into your character’s body and soul and deeply connecting to your character’s inner world. Writers must do the same thing! And we can get to this deeper level of connection with our characters through our senses. Good writers have a knack for stepping into their characters, and it shows on the page. The characters come alive, feel real! And real-feeling characters hook readers.
So, to answer your question, I recently left The Wild Rose Press. Currently, I’m an editorial consultant for CRAFT Literary, a well-established online literary magazine, and I teach other editors at Queen’s University in Ontario, Canada, the University of California at Berkeley, and the Editorial Freelancers Association in New York City. Also I work one-on-one with writers to take their manuscripts to the next level—or the next few levels. All done remotely from my home in Athens, Georgia.
The funny thing is that I feel like I ended up in publishing by accident, even though my mom encouraged me to pursue that direction all my life. I got into publishing later in my life. In my 40s, after I already had a couple of careers and raised a family, I was accepted into graduate school and earned my Master of Arts in Professional Writing.
While in graduate school, I taught First-Year Composition, tutored writers, and volunteered as a poetry editor for a little literary magazine. On the side, I was coding and designing websites. Then I volunteered for SurfCoaches, a surfing company in Costa Rica, and created a digital magazine and website for them.
Those experiences gave me the confidence to approach the Georgia Writers Association and propose a digital literary magazine. They were thrilled since they only had a little newsletter at the time. I got a team together—mostly volunteer editors and readers—and we poured through submissions. We published poetry, short stories, and articles on the craft of writing. We did a couple of flash fiction contests too. A lot of fun!
Initially, I was just going to handle the poetry side, but surprisingly to me, I ended up being really good at fixing red-hot messes and fine-tuning short stories.
One of the accepted short-story authors asked me to edit her full manuscript. Then another asked and another. They referred me to their writer friends, and before I knew it, I was working with a writer every month while still in grad school. It spread by word of mouth. Soon writers asked me to come and talk at their writer groups, and I got even more clients. Then I started presenting at writer conferences, and my career took off from the exposure and experience. I’m booked two months or more in advance now.
A few years ago, I sent letters of introduction to a few university presses and small traditional publishers. I was hired on with The Wild Rose Press and got on the developmental editor list with the University of Georgia. During the first few years, I asked myself, “Is this real? Can I do it again next month?” And I always did. My mom would say, “I told you so.”
I’m still amazed at how I get to do what I love and I can do it from home, the coffee shop, the mountains—maybe the moon in five years. (Just kidding about the moon; I’ll settle for an island as long as I have a good internet connection.)
In college, I wanted to major in Biology. My mother bucked. She said, “But you can’t; you’re a girl!” Hard to imagine nowadays! She convinced me to major in English at Loyola University in New Orleans. Eventually, I rebelled, and I secretly enrolled in college for aeronautical science to become a commercial pilot like my father. I didn’t tell my mom until after my first solo! I flew turboprops and Lear Jets for a little while, and then life took unexpected twists and turns that led me to my current publishing career.
I’m still a FAA Certified Flight Instructor and have been for almost three decades now. Being a jet pilot is a bonus in the editing world. Aspiring authors often mention that my flying past was one of the deciding factors that made them pick up the phone and ask about my editorial services. And they always sign on.
Needless to say my mom was right. She knew I had a knack for writing and editing. Don’t you hate it when your mother is always right?
DB: What attracted you to editing?
VM: Although I edit at all levels—from developmental to proofreading—I’m most attracted to developmental editing. Developmental editors are all about the big picture. We assess how scenes hang together as a whole, how a story moves and unfurls, how characters drive the story forward. We’re kind of like detectives. We look for clues—or story seeds, as I call them.
These story seeds are often hidden or not fully fleshed out by the writer. But developmental editors look deep into the heart of a story and pull them out. Often writers don’t even know these seeds are there! Their creative subconscious scattered those seeds, but their consciousness was barely aware of them. When I point them out, their faces light up. It’s incredible to watch authors in this moment of inspired realization.
What I love the most about developmental editing is these light-bulb moments.
It’s deeply fulfilling to help writers fulfill their dreams. If a manuscript lacks focus, I’ll help the writer find it. If an author lacks confidence, I’ll work to inspire, challenge, and cheer them on. A developing editor’s job is not just about the manuscript—a large chunk of what we do involves inspiring the author’s voice and developing their full potential. In fact, the best developmental editors become the author’s collaborating partners—we hone the writer’s unique voice and make the author’s vision our vision.
When copyeditors move to developmental editing, it’s a significant perspective shift for sure. And how to make that move is a big part of my focus when teaching other editors to do what I do.
DB: When reading manuscripts, what qualities catch your attention?
VM: Well, on that first page, I’m crossing my fingers and hoping to be hooked. I love a story that starts with a strong voice—either a strong narrator voice or a strong character voice. Voice is a bit of an allusive term. What a good voice is for one editor may not be for another. It’s often very subjective.
In Voice: The Secret Power of Great Writing, James Scott Bell says that a “great voice is symbiotic,” meaning interdependent, and he encourages authors to identify with their characters so intimately that the authors begin to feel and think how the characters feel and think. Again, this is what actors do when preparing for a new part, and what I try to do in my workshops.
Furthermore, I love a story that captures my senses. At The Wild Rose Press, we have a good rule of thumb: include three sensory details per page and one of those should be something other than visual. Sensory details make the characters and their world come alive and really pop off the page.
DB: What qualities turn you off?
VM: Simply boring writing. Boring is also an elusive term too. What boring is for one editor may not be boring to another editor. Again, it’s often very subjective. But there are a few things that all editors will agree on.
For instance, dialogue that doesn’t add anything to the mood or increase the tension or drive the conflict. Boring dialogue and “talking heads” turn me off the most. Talking heads is when characters are talking but disconnected from the story world—there are no action beats, no sensory details, no glimpse into the point-of-view character’s inner world and motivations. The characters don’t feel real!
But the good news is it’s an easy fix. Writers can just look for long stretches of dialogue, and weave in actions and details to ground the reader in the story’s physical world. Then show the character’s conflicting desires, values, and emotions so the character becomes real.
Another turn-off is when the characters’ roles are generic, stereotyped, or old-fashioned because they don’t represent real people in all their colors, patterns, and quirks. Again boring.
DB: Could you describe your acquisition process at The Wild Rose Press?
VM: Every editor at The Wild Rose Press may have a different process. Typically, a senior editor or our editor-in-chief will send us a potential new author’s submission package consisting of the query letter and the first five pages. Each editor makes their own decision to request more pages or send a friendly (but often helpful) rejection letter. That’s why an author’s opening pages have to pop. Writers have a small window to hook a publisher and make the acquiring editor want to read on.
However, my submission process normally starts at a writers’ conference. Most of the submissions I read were sent to me from authors I met at a conference or workshop. I also get contacted by literary agents who pitch their client’s novels.
When I receive a submission, the first thing I do is read the first five pages. Often, I can tell on page one if it’s going to be a rejection—cold hard truth. If the opening doesn’t pop off the page, most readers aren’t going to wait until page three hundred to see if anything happens. One time, a writer told me, “But it gets good on page one hundred.” True story! Readers read for the joy and thrill of it. We want that joy and thrill on page one, page two, page three, and every page after that.
To get your foot in the door with an acquisition editor, rock the house down on the first page. It doesn’t have to be exploding bombs, car chases, shooting matches, and murder mayhem on page one, but it does need to hook us immediately and keep hooking us on every page.
The hook can be a promise of future conflict or subtle micro-tension or a strong character voice. One of those three things (preferably all three) will prompt me to immediately email the author and ask for a partial or full manuscript.
After reading the first five pages, I look at the pitch part of the author’s query. I’ll also read the synopsis and then request more pages or send a rejection. Some editors always read the query first and only ask for more pages based on the pitch. However, more than once, I’ve been thrilled by a fantastic pitch and strong synopsis, only to be disappointed when reading the manuscript. I think sometimes authors hire a professional query and synopsis writer.
I suggest writing it yourself. You have to know your story cold. When writers struggle to put the gist of their stories into a strong pitch paragraph or break the story down into a tight synopsis, then I bet there is a good chance their manuscripts have plot holes or too many storylines or too many characters—just my two feathers. I’m sure there are exceptions.
If I’m on the fence about a story or just want another opinion, I sometimes run it by our reading panel for their input. Depending on their positive reviews, I will continue with the acquisition process. Sometimes the readers give me insights I haven’t thought about or clue me into some aspects of the novel that might rub readers the wrong way.
Once I find a manuscript that I love and want to make an offer to the author, I send a Request for a Contract to my senior editor. If she approves, she sends it through, and an offer is made. Then the fun begins!
DB: What do you believe are the most significant changes in the publishing industry in the past five years?
VM: Well, the pandemic certainly changed things and pushed readers more strongly toward audio and digital books. Both have been steadily rising, but they really jumped up in readership during the pandemic. Audiobooks are a hot marketplace ticket! We are talking about a billion-dollar market here!
Authors may want to consider keeping their derivative rights. Derivative rights are the starting point for audiobooks. Before signing a publishing contract, ask, “Do I control my derivative rights, specifically my audio rights?” Read that contract and consider renegotiating to hang on to those rights. Because as I said, audio rights are hot right now and are expected to get hotter.
Spotify is buying Findaway and is really moving into the audiobook market. They expect audiobook sales to grow from $3.3 billion to $15 billion by 2027. That’s huge!
If you control that right, you get 100% of the profit. However, more publishers are keeping those rights. But it’s still economically not attractive for many publishers to produce audiobooks, so they may decide not to do it. In either case, you may want to ask for those rights to be reverted back to you so that you reap all the profit.
DB: What trends have you noticed lately?
VM: TikTok is the fastest-growing social media platform and is probably today’s essential tool for branding and marketing your novels. I used to rave about Twitter, but TikTok is stealing the show these days.
Although audiobooks and digital books are hot, print books are in demand, and apparently there is a shortage. Despite the surge in new technologies, all generations still prefer reading physical books. So, the good news is that print publishing is not dying as many had predicted.
Serial fiction is super-hot! As the old sales adage goes: It’s easier to keep an old client than to get a new one. The same goes for readers. This is particularly important for self-published authors. Sites like Kindle Vella, Wattpad, Inkitt, Tapas, Radish, and other online reading apps will continue to do well.
During the pandemic, book sales increased, especially among Gen Zers. Not surprising with more free time and people working from home or off work and going to school from home. And contrary to popular belief, Millennials are voracious readers.
The book industry is still alive and well. Older readers tend to gravitate to thrillers, mystery, and suspense, whereas younger readers tend to favor fantasy, science fiction, and general literature. Young adult novels had the most significant jump in sales in 2021. Also, 66% of poetry book buyers are under thirty-four. These young people are huge readers!
One interesting statistic I found is the rise in romance readership among young people, specifically young adult men. However, with that being said, most fiction readers are still women. About 80%!
Writers may want to think about creating a tough, wicked-smart female protagonist who solves her own problems and doesn’t wait for the knight in shining armor. I think the days of the damsel in distress are gone—again, just my two feathers.
It’s good to understand the differences between the generations and how they hear about novels. Gen Z looks to social media and friends for book recommendations, whereas most of the older generations depend on bookseller lists. So, if you’re not on social media, such as BookTok, I encourage you to get hopping. It’s never too late or too soon to start.
DB: Is there anything you’d like to add that I haven’t asked about?

VM: Yes! On behalf of all editors everywhere, I want to thank you and all the writers out there. Thank you for letting us into your creative worlds. I know how hard it is to let your “baby” go and entrust it to the care of an editor. I want to acknowledge the guts it takes to be a writer and put yourself out there. I’m so happy that you are in the world! Keep learning. Keep pushing your boundaries. Keep moving forward one page at a time.
You can find me on Twitter at https://twitter.com/editorvmathews and Instagram https://www.instagram.com/val_mathews/.
~~~
Val, thanks for the deep dive into the mind of an editor. We appreciate you sharing your insights with TKZ!
~~~
This is my last post before TKZ goes on our annual holiday break. See you in 2023. Aargh! How did 2022 whiz by so fast?
As always, thank you for your interest and participation in TKZ’s community!
May your holiday season be filled with cheer, love, and peace!






 Go on a global search-and-destroy mission for the following words/phrases:
Go on a global search-and-destroy mission for the following words/phrases:






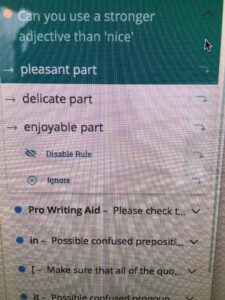
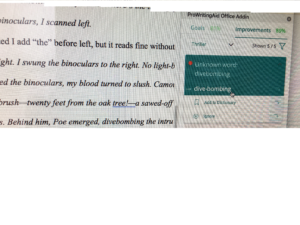
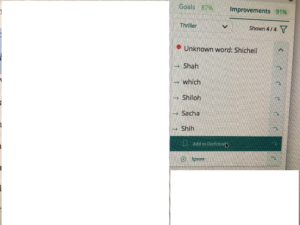
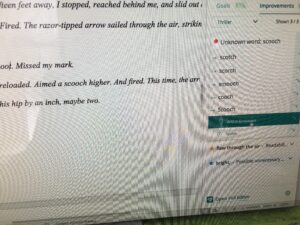
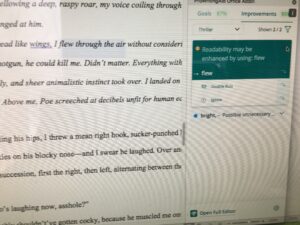
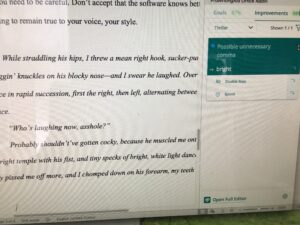
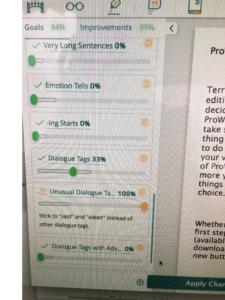
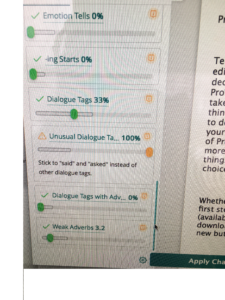
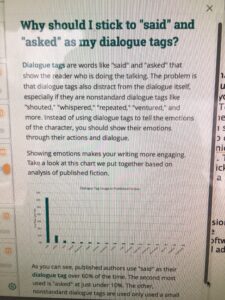
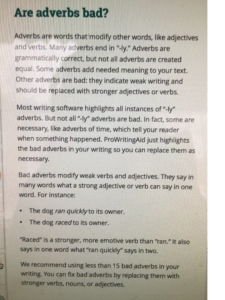
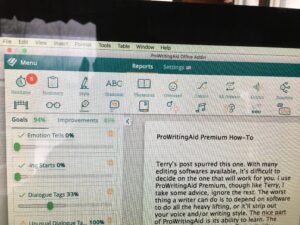
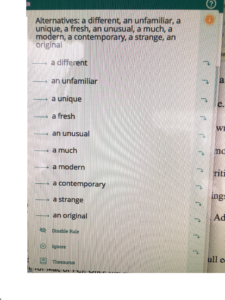


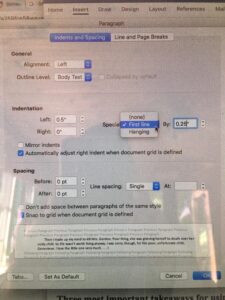
 An interesting discussion arose while working on copy edits for
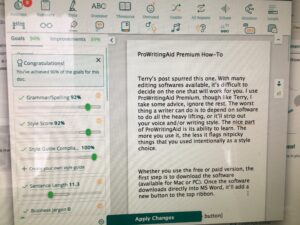
An interesting discussion arose while working on copy edits for 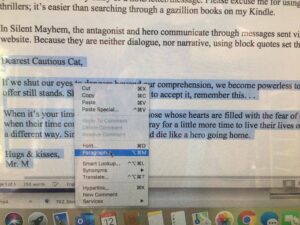 Choose “paragraph” and this screen will pop up…
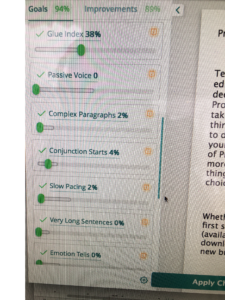
Choose “paragraph” and this screen will pop up…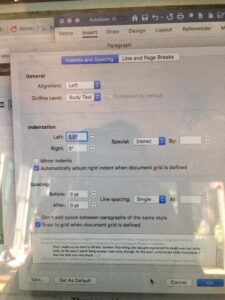
 And that’s it. Easy peasy, right?
And that’s it. Easy peasy, right?

