By SUE COLETTA
Lately, I’ve been consumed by my WIP. It happens with every book. You know the drill. At a certain point something inside takes over. No more struggling, no more hair-pulling, no more research trips down endless rabbit holes. Instead, we spend more time “in the zone” than out of it.
Keep that in mind while I share this conversation between me and my husband, Bob — with pics!

He’d just stretched out after a long day doing tile work as a favor for a friend, so exhausted he didn’t have the energy to take his boots off yet.
I’m sitting across from him. And within seconds, I’m enthralled by his boot treads. I can’t tear my gaze away, my mind whirling with endless scenarios of how I might use them in my WIP.
Bob: Why’re you staring at my boots?
Me: How long have you had those? Didn’t I buy ‘em, like, two Christmases ago?
Bob: Yeah. Why?
Me: Two years … gee, I woulda thought you’d have more of wear pattern by now. You must walk fairly even.
Bob: Thanks, I think.
It was more of an observation than a compliment, but he didn’t need to know that.
Eyes in a squint, I lean in to study the details of each tread, searching for any anomalies I could use.
Bob: What’s so fascinating about my boots?
I thumb the camera on my iPhone and aim at the treads. “Straighten your feet.”
Bob: In your mind, they’re bloody, huh?
Me: Why do you always assume the worse?
Okay, fine. Maybe I was envisioning blood in the grooves, but nobody likes a show off. 🙂 My main focus, however, was the type of impression these specific boots would leave in snow. At a crime scene, if footwear evidence is found and collected, examiners can compare these unknown impressions to known impressions, collected from other crime scenes and stored in databases.
To do this, examiners use three main characteristics for analysis …
Class characters result from the manufacturing process and are divided as “general” —characteristics that are standard for every item of that make and model — or “limited” — any variations that are unique to a certain mold. Two boots may have identical tread patterns but may also hold slight differences due to imperfections in the molds during manufacturing.
Back to Bob’s boots for a moment. This time, let’s zoom in …

See that tiny dot on the “S” in Sorel? On his right boot it’s on the bottom. On his left, it’s at the top. The “O” is filled in on the left but not on the right. Also on the right, it almost looks like there’s an apostrophe after the O, as if the brand spells its name as So’Rel. These imperfections are the perfect example of class characteristics.
Individual characteristics are unique to a particular shoe that’s worn from use, not manufacturing. Suppose someone steps on a nail. That nail hole is there for the life of the shoe, and that mark will show in the impression. Same holds true for a cut or gouge from stepping on something sharp, like broken glass. Even a small stone or twig stuck in the grooves of the tread will transfer to the impression.
Wear characteristics result from the natural erosion of the shoe caused by use. Specific wear characteristics include the wear pattern, the basic position of tread wear, the wear condition, the amount of depth of the wear, and the damage to, or destruction of, the tread pattern. The location and amount of tread loss varies for each individual, wearing that particular brand and style of shoe, based on how and where they’ve walked and the length of time they’ve owned the shoe.
Footwear impressions provide valuable information for investigators …
- Where the crime occurred
- Number of people present at the scene
- Direction the suspect traveled before, during, and after the crime
- Link other crime scenes to the same suspect
Prints are divided into three types …
A visible print is exactly like it sounds. These prints can be seen by the naked eye. Think: bloody shoe prints across a linoleum floor.
A plastic print is a three-dimensional impression left on a soft surface, like in sand, mud, or snow.
A latent print is one that’s not readily visible. It’s created through static charges between the sole of the shoe and the surface. Examiners use powders, chemicals, and/or alternative light sources to find latent prints. Think: a burglar’s shoeprint on a window sill.
The FBI compiles and maintains a footwear (and tire tread) database, which contains manufacturers’ information, as well as information from previously submitted evidence. But did you know the National Institute of Justice also maintains various forensic databases? They sure do. Which is perfect for an amateur sleuth character who doesn’t have access to the FBI’s database.
For print impressions, the NIJ maintains three databases called …
- SoleMate
- TreadMark
- TreadMate (for tire impressions)
For detailed information about how each database works, here’s the link to help with your research.
Knowing the basics of footwear impressions, I thought I was all set to write my scene. But if experience told me anything, it’s that a hands-on exercise trumps imagination. Hence why I’ve trapped myself in a steel drum to experience my character’s terror. And why, after spotting the boots, I dragged my poor husband outside to make prints in the snow.

Turns out, he had more of a wear pattern than I thought. After close inspection of several prints, worn spots in the grooves of the heel, toe, and instep revealed themselves. Guess someone doesn’t walk evenly after all. 🙂
If Bob hadn’t stretched out after work with his boots still on, and I wasn’t sitting across from him, consumed by my WIP, my story wouldn’t’ve taken a hard-right turn and led to several intense, gripping scenes. And I probably wouldn’t have written this post, either. Isn’t it amazing how that works?
We writers need to remain open to outside stimuli. If your short on ideas, you’re not paying attention to the world around you. Look through the writer’s lens at all times. That’s the biggest takeaway from this post (outside the helpful info. re: footwear impressions ;-)).
Our experiences bleed through every page we write. So, go ahead and drag your spouse/neighbor/friend into the snow to make prints, if that’s what you need for research. Or pause to listen to the throaty rattle of a raven, if you need a moment of clarity. Life is our greatest ally. Don’t squander the gift of perception by ignoring her.
Has real life ever collided with your fiction? Are you viewing the world through a writer’s lens? Please share a brief sliver of time. Like when a raindrop catches kaleidoscope colors as it rolls down a windshield or how the neighbor’s cat only limps when his owner’s watching.

 A recent conversation with my husband brought up two important points for writers to keep in mind. Rather than tell you, I’ll peel back the veil and let you eavesdrop.
A recent conversation with my husband brought up two important points for writers to keep in mind. Rather than tell you, I’ll peel back the veil and let you eavesdrop.
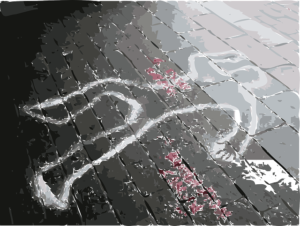



 The forensic community works tirelessly to improve techniques to aid law enforcement, and much of this work is done at
The forensic community works tirelessly to improve techniques to aid law enforcement, and much of this work is done at 