
Monthly Archives: December 2022
The Year Behind and The Year Ahead
by James Scott Bell
@jamesscottbell
 Here is the last TKZ post of the year. We will be taking our annual two-week break, and gather again on January 2, 2023. It seems apt, then, to take a look in the rearview and also through the windshield. Where have we been, and where are we headed?
Here is the last TKZ post of the year. We will be taking our annual two-week break, and gather again on January 2, 2023. It seems apt, then, to take a look in the rearview and also through the windshield. Where have we been, and where are we headed?
2022
What a year. Sometimes it felt like the cruise of the Lusitania; at other times, like an old wooden roller coaster about to be condemned. There were all sorts of moments:
- Russia invaded Ukraine. Kim Kardashian and Pete Davidson broke up. Hordes of Twitter users seemed unable to determine which was worse.
- Speaking of Twitter, some car guy bought it.
- Will Smith slapped Chris Rock.
- Johnny Depp used the term “a grumpy” in open court.
Some notable deaths were: Queen Elizabeth, Angela Lansbury, Bill Russell, Sidney Poitier, and the last great spitballer, Gaylord Perry.
Other deaths included decorum, nuance, and rationality.
And over in the publishing world—
Print Book Sales Were Down
According to Publishers Weekly:
Unit sales of print books fell 4.8% through the first nine months of 2022, from the comparable period in 2021. Unit sales dropped from 570 million copies sold in the January through September period in 2021 to 542.6 million in 2022 at outlets that report to NPD BookScan. The sales decline slowed during the third quarter, falling from a drop of 6.6% in the first half of 2021. The decline also follows a year in which unit sales for the full year rose 8.9% over 2020.
Ebooks and Audio
Ebook sales are notoriously difficult to quantify, because Indie and Amazon stats are largely hidden. With trad pub, ebook revenues were down 6.7% as compared to the first eight months of 2021. Audiobooks sales, however, were up 5.5%.
Indie sales generally may not have been spared the downward trend. Why? While sales were up during lockdown mania, when people couldn’t go out to bookstores, it seems 2022 saw a reversal of this trend. Coupled with challenging economic times, sales of just about everything were down. It feels a bit like 2008-2009. One blog lists several factors affecting book sales, e.g.,
- Looming recession
- Inflation
- Collective fatigue
- Demand saturation, tapering-off growth
- Declining old-guard ad platform effectiveness
The blog suggests that “if consumers are spending less, it might not be the time to ditch Kindle Unlimited if you’re established there and it’s been good to you, as people will cancel their subscriptions last.”
Dedicated Ebook Readers Are Dying
Nook is on life support. Kobo is mostly in Canada. Kindle still dominates, and Amazon just released a cool new model. But it appears that phones and tablets are replacing e-readers.
While that transition does not affect ebook reading per se, it does make formatting a most important consideration. Your books have to be readable on the smaller phone footprint. I use Vellum, which takes care of that problem. What are you using?
Bestsellers Are Getting Shorter
Interesting data from the analysts at Wordsrated:
- Bestsellers are getting shorter – the average length of the NYT bestseller decreased by 51.5 pages from 2011 to 2021, from 437.5 to 386 (11.8%).
- Long books (over 400 pages) are disappearing – the share of long bestsellers went from 54% in 2011 to 38% in 2021, a 30% drop.
- Long books stayed 4.4 weeks longer on the bestsellers list than short books (under 400 pages) until 2016. Since 2016, short books have been on the list 1.9 weeks longer than long books.
(Mr. Rogers Voice): “Can you say ‘shrinking attention spans’? I know you can.”
That’s good news for indie writers of pulp-style fiction. Instead of two books at 90k each, they can do three books at 60k—and charge the same price for each one.
The Big Antitrust Case
You all heard about the DOJ going to court to stop the proposed merger of Penguin Random House and Simon & Schuster. But did you understand it? Without going into massive detail, antitrust law (according to the DOJ itself) “prohibits business practices that unreasonably deprive consumers of the benefits of competition, resulting in higher prices for products and services.”
But the way this case was presented was to protect that slice of authors who command advances of $250,000 or more. Is that you? I didn’t think so.
The trial was marked by the testimony of CEOs and agents and one Mr. Stephen King, who said:
I came because I think consolidation is bad for competition. That’s my understanding of the book business, and I’ve been around it for fifty years. When I started in this business, there were literally hundreds of imprints, and some of them were run by people with extremely idiosyncratic tastes, one might say. Those businesses were either subsumed one by one or they ran out of business. I think it becomes tougher and tougher for writers to find enough money to live on.
(For a summary of the key events of the trial, see the coverage by Publishers Weekly.)
The DOJ won. PRH has decided not to appeal. In reading Judge Florence Tan’s decision, a few things jumped out at me:
- Only 35 out of every 100 books published turns a profit.
- “Breakout” titles — those books that “outstrip” expectations — are what make up most of a pub company’s profit.
- The trad model is to acquire a large number of books, knowing that most titles will not be profitable, and hoping for that big home run, like Gone Girl.
- PRH CEO Markus Dohle testified that publishers are like “angel investors” that “invest every year in thousands of ideas and dreams, and only a few make it to the top.” When a book is a breakout, it allows the company to take risks in acquiring new books and “betting” on new titles.
- And this, from pg. 19: “Self-publishing is not a significant factor in the publishing industry. Self-published books are rarely published in print and are typically limited to online distributions. The authors of self-published books cannot pay themselves an advance. [JSB: But they get a 70% royalty and get paid every month!] Moreover, individual authors generally do not have relationships with media or distributors necessary to ensure that their books are visible to a potential audience.” [JSB: How often does a fiction author get on The Today Show?]
So what does all this mean for writers who don’t command huge advances? The ever-insightful Jane Friedman, in her Hot Sheet newsletter (subscription required) says:
All along, I’ve said in this newsletter (and elsewhere) that I don’t think this case has much or any bearing on the average author’s earnings. While I can’t speak to the legal merits of the government’s case, I’ve never been convinced that blocking this merger would save anything of value that wasn’t already lost decades ago, when industry consolidation began. Nor is anyone arguing, as far as I’ve seen, that preserving the advances of authors who receive $250k+ will have positive trickle-down effects for the entire literary ecosystem.
2023
On Predicting the Future
“People ask me to predict the future, when all I want to do is prevent it. Better yet, build it. Predicting the future is much too easy, anyway. You look at the people around you, the street you stand on, the visible air you breathe, and predict more of the same. To hell with more. I want better.” – Ray Bradbury
“The only way you can predict the future is to build it.” – Alan Kay
“I never think of the future, it comes soon enough.” – Albert Einstein
“The future belongs to those who believe in the beauty of their dreams.” – Eleanor Roosevelt
So How Do You Earn More Dough Next Year?
1. Within The Forbidden City
In traditional publishing, it used to be said you needed four to five books getting an increasing foothold among readers to move toward significant writing income. See The Career Novelist by agent Donald Maass.
In these latter days, however, an author has one or maybe two chances. As the DOJ case revealed, the big pubs want home runs, and want them out of the gate. They generally won’t put any significant marketing money into most books unless and until those books show some momentum on their own.
So write a home run and you’re golden.
If not, and you are shown the gate by the Forbidden City elders, there are many smaller publishers out there who will allow you singles and doubles, and a shot at building a readership.
2. Indie
Want to know what it takes to bring in some good lettuce as an indie writer? I found the information in this survey instructive (h/t Joanna Penn for the link). It confirms my own experience. It’s worth your time to have a look.
Still and all, one truth remains: the best marketing, in either world, is word of mouth, which comes from the books themselves. Meaning—
Stick to The Fundamentals
From time immemorial, writers of fiction have known that the fundamentals for success are basic: be good and be productive.
To be good means always growing in your craft. Assess your work vis-à-vis the seven critical success factors of fiction—plot, structure, characters, scenes, dialogue, voice, and meaning. Figure out what needs improving (and remove any chips on your shoulder) and then set about to study those areas and practice what you learn.
As for production, you don’t have to write a novel every month. Just be consistent. A page a day is a book a year. Determine how many words you can comfortably write in a week. Up that by 10% and make it your weekly goal. If you miss a day, make it up on other days. If you miss a week, fuggetaboutit. Start fresh on Monday.
Develop ideas even as you’re working on your WIP. Be like a movie studio, with one “green lit” project, a few “in development” and a few that are one-line pitches.
Most of all, nurture the joy factor and love what you do.
Have the mindset of the pulp writers of yore, who didn’t have time to whine or moan during the Depression. They had to eat, so the wrote. And looked at the enterprise as a business. One of those writers was W. T. Ballard, who wrote for Black Mask. In an interview later in life he said:
My views on writing as a business? That it is not much different from any other. You have to keep swinging, rolling with the punches, keep alert and attuned to the changes that take place suddenly or gradually, but always constantly.
Words for writers to live by.
Now from all of us at TKZ: Thank you, loyal readers, for another great year. We have some of the best, most informed, and most interesting commenters in the entire blogosphere. Let’s continue the conversation in 2023. May abundant blessings be yours this holiday season. See you soon!
Tis the Season for Holiday Words of Wisdom
One of my favorite times of year is almost here—the stretch of days from Christmas Eve through New Year’s Day. Here in the Pacific Northwest, we can have rain, frost, snow, even clear and sunny weather. A special time of year to spend with friends and family. Today it’s my good fortune to share past holiday-themed insight and advice from members of our Kill Zone Blog family.
First, Jordan Dane provides “Holiday Food for thought on character conflicts, with great advice on finding and deepening those conflicts. Then, P.J. Parrish asks if your “Book is a Christmas Sweater” in the description department, and discusses how to dress your writing for success. Finally, Debbie Burke gives “Five New Year’s Techniques On Avoiding Butt-in-Chair Syndrome” from 2018.
I encourage you to check out the full posts for each (date linked below) and comment on them. I hope they provide an inspiring basis for discussion today.

What does your character want and why can’t they have it? Conflict is vital to creating memorable characters. No conflict(s), no story. I can’t emphasize this enough. If there is a common mistake many aspiring authors make, it’s not having enough conflict to keep a story flowing through to the end that will drive the characters and keep their story interesting.
Your EXTERNAL CONFLICT might be the villain or the insurmountable situation, but the most unforgettable characters will also contend with their own flaws or biases (INTERNAL CONFLICTS) or demons, so they have a journey toward self-discovery. If you have a hero who is in conflict with a villain, while he’s battling his own demons, then think about creating a heroine who has opposing conflicts where one of them must lose in order to be together. Conflicts are best when layered and made more complicated.
Find your characters’ greatest weaknesses or fears—their internal conflicts—and demand they deal with it. Torture them. It’s legal. Rubbing their nose in it generally comes from the influences of the external conflict—the plot. The one-two punch of the external and internal conflicts adds depth to your character. Make him/her suffer, then ramp up the stakes and the tension. It’s all about drama!
Add Depth to Each Character—Give them a journey
• With any journey comes baggage. Be generous. Load on the baggage. Give them a weakness that they’ll have to face head-on by the climax of the book.
- Make them vulnerable by giving them an Achilles Heel. Even the darkest street thug or a fearless young girl with magical powers should have a weakness that may get them killed and certainly makes them more human and relatable.
- Whether you are writing one book or a series, have a story arc for your character’s journey that spans the series. Will they find peace or love, or some version of a normal life? Will they let someone else into their lives or will they be content to live alone? Will a villain have a chance at redemption? Do what makes sense for your character, but realize that their emotional issues will cloud their judgment and affect how they deal with confrontations. By the end of a book, they should learn something.
Use Character Flaws as Handicaps
• Challenge yourself as an author by picking flaws that will make your character stand out and that aren’t easy to write about. Sometimes that means you have to dig deep in your own head to imagine things you don’t want to think about, but tap into your empathy for another human being. You might surprise yourself.
- Stay true to the flaws and biases you give your characters. Don’t present them to the reader then have the actions of the character contradict those handicaps. Be consistent. If they have strong enough issues, these won’t be fixed by the end of the book. Find a way to deal with them.
Jordan Dane—December 6, 2018
So how do you find your happy medium? How do you know when you’ve gone too far or haven’t gone far enough? How do you resist gilding the lily? There are no easy answers but here are a few things to think about:
Don’t generalize: Try to avoid abstractions. Be concrete in your descriptions. Instead of saying someone played a board game, say it’s Monopoly. Instead of a “bad smell” use the specific “like sour milk.” But again, don’t reach too hard or you look silly.
Don’t forget to compare and contrast. The secret to originality is the ability to see relationships. If you’re describing something green, it’s your job to come up with something fresher than “grass.” Here’s one of my faves from Steinbeck: “The customers were folded over their coffee cups like ferns.” And come to think of it, Alice’s description of Calvin Coolidge as “looking like he was weaned on a pickle” is pretty good. But again, don’t strain for originality or you just sound pretentious.
Don’t lean on adjectives: Just lining up a string of modifiers is lazy writing. (ie tall, dark and handsome). Try to find one vibrant adjective rather than several weak ones. But again, don’t strain or reach for the Thesaurus. Sometimes a lawn is just a lawn…not a “verdant sward.”
Don’t use cliches: It’s easy to slip into tired, flabby words. If you want to say something is white, you can’t use “white as snow.” It’s not yours! Neither is “thin as a rail, sick at heart, hard as a rock” or even “overcome with grief.” Time has eroded all those. It’s your job to find new ways of making your reader experience your fictional world.
Yeah, it’s tough to dress your writing for success. But don’t despair. Description is one of the things that you can get better at. Believe me, I know. I used to lard my paragraphs with lovingly crafted images that dammit, were going to stay in there because I worked so hard on them. But then my sister told me one day that I was — ahem — dressing to impress. I made every writer’s biggest mistake: I fell in love with the sound of my own voice and was trying to be “writerly.”
Finding your style — be it writing or fashion — is a lifelong process. When I went to my prom, I looked like a cross between Scarlett O’Hara and a Kabuki dancer. Through practice, I look a little better these days. Likewise, in my writing, I have learned what to leave off, what to cut out. In fact, I have gone too far with my WIP so my critique group friends tell me I am now underwriting and they are advising me to add more description.
P.J. Parrish—December 17, 2013
Vision
Do you have 20/20/20 vision? No, that’s not a typo, but rather an exercise suggested by eye doctors to counteract eyestrain and blurry vision from too much screen time.
Every 20 minutes, look away from your screen to an object at least 20 feet away and focus on it for at least 20 seconds.
For more eye exercises, check out: http://www.allaboutvision.com/cvs/irritated.htm
And finally, my favorite exercise…
Go for a walk
When you take your dog for a walk, she knows what she’s supposed to do. The writer’s brain can be trained and reinforced with praise the same way you train your pooch. As you move muscles and increase blood flow, your brain expels waste.
I confess during walks I’ve left many hot, steaming piles along the pathway. The best part is, unlike the dog, I don’t need a baggie to pick them up!
Once waste thoughts are cleared out, there’s room for new ideas and solutions to bubble up from the subconscious (Check out Jim Bell’s classic post about “the boys in the basement”).
Start training your brain with a small problem: let’s say you’re seeking a particular word that’s eluding you, despite searching the thesaurus. Go for a short walk and let the brain relax. After a few minutes of exercise and fresh air, the elusive word often pops up from the subconscious.
Give yourself a pat on the head and praise, “Good brain!”
A Milk Bone is optional, your choice.
Pretty soon, the subconscious learns that when you take a walk, it’s expected to perform, just like Fifi. While it sniffs the bushes and chases a squirrel, it’s also learning to deliver fresh ideas and solutions. The more you positively reinforce the subconscious for its results, the better and more frequently it comes up with solutions.
Walking works for me 100% of the time because my brain is conditioned. If I’m stumped about what a character should do next, or if the plot gets lost down a rabbit hole, I take a spin around the neighborhood. Before long, the uncertain character now knows her next move; or the rabbit hole has led to an unexpected escape route. I can’t wait to rush back to the keyboard eager to implement the solutions my subconscious offered up.
Debbie Burke—January 25, 2018
***
There you have it– putting conflict into your characters’ lives, avoiding your description becoming the literary equivalent of a Christmas sweater, and techniques to avoid the physical consequences of “butt-in-chair” time.
- What’s your sure fire way to put more conflict into your characters’s lives?
- How do you find the description “happy medium?”
- What physical challenges does butt-in-chair time pose for you? How do you mitigate any challenge?
This is my final post of 2022. I wish everyone a wonderful Holiday Season and all the best in 2023.
Reader Friday – What’s on your Christmas list?

It’s not too late. You have nine days to get your request in. Well, actually eight, if you want Santa to deliver it. And that’s if you’ve been nice.
So, what’s on your Reader/Writer Christmas list? And, as I so often do (remember, I write fantasy), we won’t place any limits on the price or performance or actual reality of your requested gift. In fact, let’s see how creative you can get. We write fiction, right?
The only requirement is that the gift request relates to your reading or writing. Okay, now tell us about your dream gift. And don’t go on too long, or Blitzen will push the time-limit buzzer. She wants to get that gift made and packaged.
Oh, I almost forgot: “Merry Christmas to all, and to all a good holiday break!”
The Bizarre Death of Gloria Ramirez — The Toxic Lady
At 8:15 pm on February 9, 1994, paramedics wheeled 31-year-old Gloria Ramirez—semi-conscious—into the Emergency Room at Riverside General Hospital in Moreno Valley, California. Forty-five minutes later, Ramirez was dead and 23 out of the 37 ER staff were ill after being exposed to toxic fumes radiating from Ramirez’s body. Some medical professionals were so sick they required hospitalization. Now, 28 years later, and despite one of the largest forensic investigations in history, no conclusive cause of her toxicity has been identified. Or has there?
The Toxic Lady case drew worldwide attention. No one in medical science had experienced this, nor had anyone heard of it. How could a dying woman radiate enough toxin to poison so many people yet leave no pathological trace?
The medical cause of Ramirez’s death was clear, though. She was in Stage 4 cervical cancer, had gone into renal failure, which led to cardiac arrest. Anatomically, the fumes had nothing to do with Gloria Ramirez’s death. But what caused the fumes?
“If the toxic emittance was not a death factor, then what in the world’s going on here?” was the question going on in so many minds—medico, legal, and layperson. To answer that, as best as is possible, it’s necessary to look at the Ramirez case facts both from what the eyewitnesses (and the overcome) said and what forensic science can tell us.

Gloria Ramirez, a wife and mother of two, was in terrible health when she arrived at Riverside Hospital. She’d rapidly deteriorated after being in palliative, home-based care with a diagnosed case of terminal cervical cancer. In the evening of February 9th, Ramirez developed Cheyne-Stokes breathing and went into cardiac arrhythmia or heart palpitations. Both are well-known signs of imminent death. Her home caregivers called an ambulance and had her rushed to the hospital as a last life-saving resort.
A terminal cancer patient, like Gloria Ramirez, was nothing new to the Riverside ER team. She was immediately triaged, and time-proven techniques were quickly applied. First, an IV of Ringer’s lactate solution was employed—a standard procedure for stabilizing possible blood and electrolyte deficiencies. Next, the trauma team sedated Ramirez with injections of diazepam, midazolam, and lorazepam. Thirdly, they began applying oxygen with an Amb-bag which forced purified air directly into Ramirez’s lungs rather than hooking up a regular, on-demand oxygen supply.
So far, Ramirez’s case was typical. It wasn’t until an RN, Susan Kane, installed a catheter in Ramirez’s arm to withdraw a syringe of blood that circumstances went from controlled to completely uncontrollable. Kane, a highly experienced RN, immediately noted an ammonia-like odor emanating from the syringe tip when she removed it from the catheter. Kane handed the syringe to Maureen Welch, a respiratory therapist, and then Kane leaned closer to Ramirez to try and trace the unusual odor source.
 Welch also sniffed the syringe and later agreed with the ammonia-like smell. “It was like how rancid blood smells when people take chemotherapy treatment,” Welch would say. Welch turned the syringe over to Julie Gorchynski, a medical resident, who noticed manila-colored particles floating in the blood as well as confirming the ammonia odor. Dr. Humberto Ochoa, the ER in-charge, also observed the peculiar particles and gave a fourth opinion that the syringe smelled of ammonia.
Welch also sniffed the syringe and later agreed with the ammonia-like smell. “It was like how rancid blood smells when people take chemotherapy treatment,” Welch would say. Welch turned the syringe over to Julie Gorchynski, a medical resident, who noticed manila-colored particles floating in the blood as well as confirming the ammonia odor. Dr. Humberto Ochoa, the ER in-charge, also observed the peculiar particles and gave a fourth opinion that the syringe smelled of ammonia.
Susan Kane stood up from Ramirez (who was still alive) and felt faint. Kane moved toward the door and promptly passed out—being caught in the nick of time before bouncing her head off the floor. Julie Gorchynski also succumbed. She was put on a gurney and removed just as Maureen Welch presented the same symptoms of being overcome by a noxious substance.
By now, everyone near the dying Gloria Ramirez was feeling the effects. Ochoa, himself now ill, ordered the ER evacuation and for everyone—staff and patients—to muster in the open parking lot where they stripped down to their underclothes and stuffed their outer garments into hazmat bags.
Ramirez remained on an ER stretcher. A secondary trauma team quickly donned hazmat PPE (Personal Protection Equipment) and went back to give Ramirez what little help was left. They did CPR until 8:50 pm when the supervising doctor declared Gloria Ramirez to be dead.
 Taking utter precaution, the backup trauma team sealed Gloria Ramirez’s body in multi-layers of body shrouds, sealed it in an aluminum casket, and placed it in an isolated section of the morgue. Then they activated a specially-trained hazmat team to comb the ER for traces of whatever substance had been released and caused such baffling effects to so many people. They found nothing.
Taking utter precaution, the backup trauma team sealed Gloria Ramirez’s body in multi-layers of body shrouds, sealed it in an aluminum casket, and placed it in an isolated section of the morgue. Then they activated a specially-trained hazmat team to comb the ER for traces of whatever substance had been released and caused such baffling effects to so many people. They found nothing.
Meanwhile, Riverside hospital staff had to treat their own. Five workers were hospitalized including Susan Kane, Julie Gorchynski, and Maureen Welch. Gorchynski suffered the worst and spent two weeks detoxifying in the intensive care unit.
The Riverside pathologists faced a daunting and dangerous task—autopsying the body which they considered a canister of nerve gas harboring a fugitive pathogen or toxic chemical. In airtight moon suits, three pathologists performed what might have been the world’s fastest autopsy. Ninety minutes later, they exited a sealed and air-tight examining room with samples of Gloria Ramirez’s blood and tissues along with air from within the shrouds and the sealed aluminum casket.
The autopsy and subsequent toxicology testing found nothing—nothing remotely abnormal that would explain how a routine cancer patient could be so incredibly hostile. The cause of death, the pathologists agreed, was cardiac arrest antecedent (brought on by) to renal (kidney) failure antecedent to Stage 4 cervical cancer. The Riverside coroner concurred, and his mandate was fulfilled with no doubt left about why and how Gloria Ramirez died.
For the coroner, that should have been it. There was no evidence linking the mysterious fumes to the cause of death, and whatever by-product was in the ER air was not a contributor to the decedent’s demise. That problem should have been one for the hospital to figure out on their own. However, the Riverside coroner was under immense public pressure to identify the noxious substance for no other reason than preventing it from happening again.
The coroner worked with the hospital, the health department, the toxicology lab, and Gloria Ramirez’s family to come to some sort of reasonable conclusion. The Ramirez family had no clue—no suspicions whatsoever—of any foreign substance Ramirez had ingested or been exposed to that could trigger such a toxic effect. The toxicology lab was at a wit’s end. They’d never seen a case like this, let alone heard of one. And the health department went off on a tangent.
The county’s health department appointed a two-person team—a team of medical research professionals—to interview every person exposed to the ER and surrounding area on February 9, 1994. They profiled those people so closely that the two-expert team even cross-compared what everyone did, or didn’t, have for dinner that night. When that preeminent probe was over, and no closer to a smoking gun than the struck-out hazmat team failed to find on the night of the fright, the interviewers came to a conclusion—mass hysteria.
The team of two medical doctors, both research scientists, concluded there was no poisonous gas. In their view, in the absence of evidence, there was only one explanation and that was that 23 people simply imagined they were sick. Some, they concluded, had such vivid imaginations that they placed themselves into the intensive care unit.

This was the report the health department delivered to the coroner. While the coroner was now scrambling for damage control, some of the “imaginary” health care workers who could have died during exposure, launched a defamation lawsuit against the hospital, the health department, and the two investigators who concocted the mass hysteria conclusion.
Frustrated with futility, the coroner (who was way outside his jurisdictional boundaries) turned to outside help. He found it at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratories (LLNL) near San Francisco.
Lawrence Livermore initially wasn’t in the medical or toxicological business. They were nuclear weapons makers with a busy mandate back in the cold war era. Now, by the 90s, their usefulness was waning, and so was their funding, so they decided to broaden their horizons by creating the Forensic Science Center at LLNL.
Brian Andresen, the center’s director, took on the Toxic Lady case. The coroner gave Andresen all the biological samples from Ramirez’s autopsy as well as the air-trapping containers. Andresen set about using gas-chromatograph-mass spectrometer (CG-MS) analysis which would have been the same process the Riverside County toxicologist would have used to come up with a “nothing to see here, folks” result.
But Andresen did find something new to see. He found traces dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) in Ramirez’s system. Not a lot—just traces—but clearly it was there. Andresen felt he was on to something.
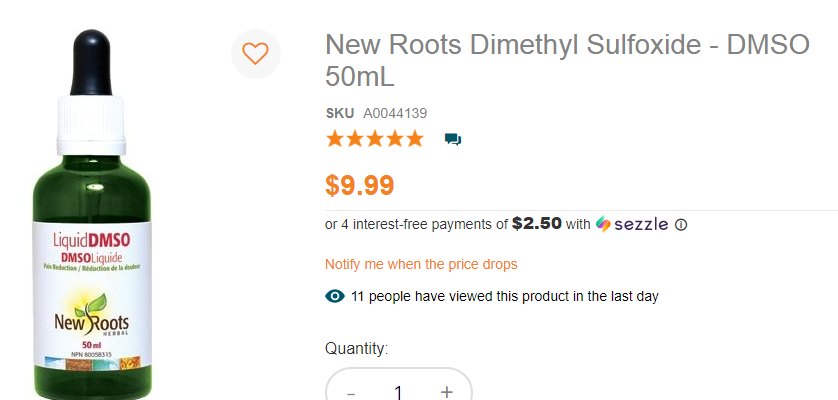
Dimethyl sulfoxide, on its own, is stable and harmless. It’s an organic sulfur compound with the chemical formula (CH3)2S0 and is readily available as a degreasing agent used in automotive cleaning. It’s also commonly ingested and topically applied by a cult-like, self-medicating culture of cancer patients. At one time, there was a clinical trial approved by the FDA to use DMSO as a medicine for pain treatment, and it was dearly adopted by the athletic world as a miracle drug for sports injuries. The FDA abruptly dropped the DMSO program when they realized prolonged use could make people go blind.
Brian Andresen developed a theory—a theory adopted by many scientists who desperately wanted some sort of scientific straw to grasp in explaining the bizarre death of the Toxic Lady—Gloria Ramirez. Andresen’s theory went like this:
Gloria Ramirez had been self-medicating with DMSO. When she went into distress at home, the paramedics placed her in an ambulance and immediately applied oxygen. Ramirez received more oxygen at the ER which started a chemical reaction with the DMSO already in her body systems.
Note: Chemically, DMSO is (CH3)2SO which is one atom of carbon, three atoms of hydrogen, two atoms of sulfur, and one atom of oxygen—a stable and harmless mix.
However, according to the Andresen theory, when medical staff applied intense oxygen to Ramirez, the DMSO chemically changed by adding another oxygen atom to the formula—becoming (CH3)2SO2—dimethyl sulfone (DMSF). DMSF, also, is harmless and it’s commonly found in plants and marketed as a dietary supplement. So far, so good.
It’s when four oxygen atoms are present that the stuff turns nasty. The compound (CH3)2SO4 is called dimethyl sulfate, and it emits terribly toxic gas-offs. This is what Andresen suspected was the smoking gun. The amplified oxygenation turned the self-medicating dimethyl sulfoxide Ramirez was taking into dimethyl sulfone which morphed into the noxious emission, dimethyl sulfate.

The coroner liked it. So did many leading scientists. The coroner released Andresen’s report as an addendum to his final report, even though all agreed that if dimethyl sulfate was gassed-off by Ramirez in the ER that made so many people sick, it had absolutely nothing to do with the Toxic Lady’s death. The coroner closed his file, and the finding went on to be published in the peer-reviewed publication Forensic Science International.
There were two problems with Andresen’s conclusion. One was more scientists were disagreeing with it than agreeing. Some of the dissenters were world-class toxicologists who said it was chemically impossible for hospital-administered oxygen to set off this reaction. Two was Ramirez’s family adamantly denied she was self-medicating with DMSO.
The Toxic Lady case interest was far from over. Many people knew DSMO would be present in minute amounts in most people’s bodies and called bullshit. It’s a common ingredient in processed food and metabolizes well with a quick pass-through rate in the urinary tract. In Ramirez’s case, she had a urinary tract blockage which triggered the renal failure which triggered the heart attack. If it wasn’t for the blockage, the DSMO probably wouldn’t have been detected.
On the sidelines, there were people—knowledgeable people—strongly saying another chemical would give the same ammonia-like, gassing-off toxins that ticked all the 23-person symptom boxes.
Methylamine.
Methylamine isn’t rare. It’s produced in huge quantities as a cleaning agent, often shipped in pressurized railroad cars, but it’s tightly controlled by the government. That’s because methylamine can be used for biological terrorism and for cooking meth.
 Yes, methylamine is a highly sought-after precursor used in manufacturing methamphetamines. Remember Breaking Bad and the lengths Walt and Jesse go to steal methylamine? Remember the precautions they take in handling methylamine?
Yes, methylamine is a highly sought-after precursor used in manufacturing methamphetamines. Remember Breaking Bad and the lengths Walt and Jesse go to steal methylamine? Remember the precautions they take in handling methylamine?
Well, back before Breaking Bad broke out, the New Times LA ran a story giving an alternative theory of what happened to make the Toxic Lady toxic. Whether the Times got a tip, or some inside information, they didn’t say. What they did say was that Riverside County was one of the largest methamphetamine manufacturing and distribution points in America, and that Riverside hospital workers had been smuggling out methylamine to sell to the meth cookers. (Hospitals routinely use methylamine as a disinfectant in cleaning agents, including sterilizing surgical instruments.)
The Times report said Riverside hospital workers used IV bags to capture and store methylamine as the IV bags were sealed, safe to handle, and entirely inconspicuous. The story theorized that an IV bag loaded with about-to-be smuggled methylamine accidentally found its way into the ER and got plugged into Gloria Ramirez’s arm. Because methylamine turns to gas so quickly when exposed to oxygen, this would explain why no traces were found in the toxicology testing—it all went into the air and into the lungs of 23 people.
———
As a former coroner, I’d be skeptical of this methylamine theory except for personal knowledge of a similar case. My cross-shift attended a death where a meth cooker had methylamine get away from him in a clandestine lab. The victim made it outside yelling for help but shortly succumbed. The civilians, hearing his cries, rushed over and were immediately overpowered with the exact symptoms as the Riverside medical people experienced.
 The first responders also succumbed to toxic fumes and had to back off. By the time my cross-shift arrived to view the body, many contaminated people were already at the hospital. My colleague made a wise decision. He signed-off the death as an accident, declined to autopsy, and sent the body straight to the crematorium—accompanied by guys in hazmat suits with the body sealed in a metal container and strapped to a flat deck truck.
The first responders also succumbed to toxic fumes and had to back off. By the time my cross-shift arrived to view the body, many contaminated people were already at the hospital. My colleague made a wise decision. He signed-off the death as an accident, declined to autopsy, and sent the body straight to the crematorium—accompanied by guys in hazmat suits with the body sealed in a metal container and strapped to a flat deck truck.
Do I buy the Times methylamine theory? Well, I’m a big believer in Occam’s razor. You know, when you have two conflicting hypotheses for the same puzzle, the simpler answer is usually correct. Some one-in-a-billion, complex chemical reaction that world-leading toxicologists say can’t be done? Or some low-life, crooked hospital drone letting an IV bag full of stolen methylamine get away on them?
You know which one I’m going with to explain the bizarre death of the Toxic Lady — Gloria Ramirez.
Kill Zoners — What do you think? Does the methylamine theory hold water? Or am I just all wet?
Writing Out of Sequence
Twenty years ago, I met Barry Livingston by way of helping him shop his industry autobiography, The Importance of Being Ernie. Barry played Ernie, the youngest Douglas child in the iconic My Three Sons television show. During my discussions with him–and through reading his book–I learned that MTS was the first television series to feature a bona fide movie star, in the person of Fred MacMurray. In those days, television was seen as a lower form of entertainment (and a huge threat to feature films). To cross over was to risk one’s career in movies.
One of the most fascinating details Barry shared with me was the fact that MacMurray’s contract stipulated that he would be on the MTS set for only a very limited number of days–this during a time when a television season ran up to 30 episodes a year! The schedule required a bizarre filming strategy. During his time on set, MacMurray shot only his scenes from every episode. If he wasn’t physically in the shot, the shot was not filmed. This meant that every angle on any scene that did not directly involve MacMurray was shot at a different time.
Think about that from Barry Livingston’s point of view: you’re six or seven years old and every reaction and every closeup of you is shot out of context and out of sequence. I haven’t seen MTS in many years, but my recollection is that he pulled it off pretty well.
Movies have always been shot out of sequence for budgetary reasons. You either shoot out a location or you shoot out a character so that you limit expenses. It seems to me that that’s much easier when the script is finished, the shots are story boarded and blocked, and all the actors have to do is, well, act.
In my most recent couple of books, I’ve experimented with writing out of sequence. In the past, I would write my books more or less as they appear in the final version, shifting POVs real time as the story unfolds. More recently, I’ve started to write straight through a POV character’s story arc, and then moving on to do the same for another POV character. At the end of the draft, I cut and paste to get the story to flow correctly.
The process works pretty well until I get to a scene where multiple POV characters are interacting. At that point, I have to decide to whom the scene belongs, and then I write the scene accordingly, giving myself an anchor point for each of the involved characters–a point to which they all must somehow arrive as I’m writing out of sequence.
A Throwback To Accident Investigation
One of my professors in graduate school was Ludwig (Ludi) Benner, who invented an accident investigation technique called Multilinear Event Sequencing (MES). In its simplest form, MES recognizes that at some point before an event, every injured person and every damaged object was at a point of stasis, where everybody and everything was okay. An instant later, an as-yet unknown event occurs (which itself is always the result of other sub-events) and the result is scattered debris and injured people.
In applying MES strategy to the investigation, every person and every bit of debris is considered an actor and is given its own timeline. If we know that a propellant mix was at normal temperature at 09:03:54:70, started to rise slowly at 09:03:54:72, spiked at 09:04:24:78, and went dark at 09:04:55:31 (followed by a big boom), we have a valuable frame of reference. The duration of the primary event was just over one minute, so that defines the timeline for the initial investigation. Every fragment of the building and the tooling will be mapped and examined. If the tooling shows signs of shear, then the explosion was low-order; if it is fractured, that points to a high order explosion, and that determination then leads to other conclusions and avenues of investigation. Bottom line: every bit of debris is the result of an identifiable force which is the result of some other definable force.
Let’s say that the explosion was the result of contamination in the propellant mix. Now, the investigation turns in that direction. With quality controls being what they are, someone somewhere made a big mistake. Every worker and outside player now gets their own timeline. If it turns out that every one of our own workers followed their protocols and procedures to the letter, we now have to turn our attention to the transportation company that delivered the components to us, and the manufacturer or distributor from which the transporter picked up the materials.
That’s a lot of timelines to keep track of, but if you’re true to the process and you’re patient, the intersections of the timelines always bring big reveals.
Plotting Is A Close Cousin To Accident Investigation
In accident investigation, you start with a set of conditions that are the result of a story the investigators labor to unfold. As an author, I start with a premise and evolve it into a disaster by creating the multilinear events that all interact with each other to create the end result I’m looking for.
Using the propellant example above, let’s say we want our hero safety engineer (why haven’t we seen more of those in fiction?) to discover that the contamination of the mix was the result of Russian sabotage. How do we get there, and how do we do it in a way that is always engaging for the reader? Here comes the reverse engineering:
- Why do the Russians want to create an explosion?
- Why choose this route instead of, say, planting a car bomb?
- How does the saboteur avert the internal quality control processes?
- What is the plotting road map that leads our hero to discover the truth?
- Once our hero learns the truth, why doesn’t he call the FBI and let them take care of things?
There are many more, of course, but the point here is that by choosing one character’s arc and writing it all the way through (or mostly all the way), you discover the data points that other characters need to find.
Is this something you’d try in your own writing?
On a personal note, this is my last post for 2022 as we head toward our Holiday Hiatus. I wish all of you a wonderful holiday season, and nothing but the best in the coming new year. If you’re into Christmas letters that run to the long side, here’s a link to the Semi-Decennial Gilstrap Christmas Letter.
Do You See Dead People?
“The detective isn’t your main character, and neither is your villain. The main character is the corpse. The detective’s job is to seek justice for the corpse. It’s the corpse’s story, first and foremost.” — Ross Macdonald
By PJ Parrish
Has crime fiction gotten…more humane?
That’s the question posed by mystery writer Matthew Sullivan. The author of Midnight at the Bright Ideas Bookstore Sullivan wrote an essay a while back asking us to consider the place empathy, especially for the victims, has in modern crime fiction. To make his point, he traces how readers’ tastes in crime fiction have changed drastically from Poe through Parker to Penny. Writes Sullivan:
From “colorless” characters whose main duty was to serve the plot to well-developed human beings with rich inner lives, this shift in the way we see victims compels readers to empathize—to be emotionally invested in the page, and to experience these lost lives in full.
This is a subject near and dear to my heart. As I’ve written before in two posts (here and here), I believe readers want fully fleshed out victims, characters they can connect with — even if they are dead. Maybe especially if they are already dead when the story begins. But I didn’t realize how much empathy has changed in crime fiction over the years until I read Sullivan’s take. He gives examples of this with comments on how audiences react to the victims. Some highlights:
- The Murders in the Rue Morgue. Edgar Allen Poe. 1841. Recluse women dead by strangulation, straight-edge razor, blunt trauma. The role that the victim will occupy for much of the next 180 years: that of a distant, “colorless” human, whose loss is not to be felt by the reader—for that would ruin all the fun. Readers’ emotional response: Conveniently cold. And the genre begins…
- The Maltese Falcon. Dashiell Hammett. 1929. Miles Archer shot right through the pump with a Webley .38 revolver. When Sam Spade learns that his partner has been murdered, Sam slips right into the first two stages of grieving: lighting a smoke and cracking his knuckles. Readers’ emotional response: Rest in peace, chump! You shoulda seen it comin’.
- And Then There Were None. Agatha Christie. 1939. Anthony Marston poisoned (of course). There’s a good reason why Christie has 2 billion books in print, but with victims that are often scoundrels, and often under-developed, it’s little wonder that readers rarely weep over the body in the library. Readers’ emotional response: Deeply amused, thoroughly puzzled, but definitely not losing any sleep.
- The Talented Mr. Ripley. Patricia Highsmith. 1955. Antihero weasel Tom Ripley bludgeons Dickie to death in row boat then steals his identity. Readers’ emotional response: Downright ashamed of ourselves, especially as Ripley comforts the distraught parents of the young man he killed. Psychological suspense at its—worst?
- Twin Peaks. David Lynch 1989. Laura Palmer stabbed and abandoned on a beach wrapped in plastic leads the viewer into a hall of mirrors but the theme comes through clearly, just as it does in many contemporary mysteries — the ripple effects of crime. From high school hallways to booths at the diner, everyone is impacted by the shockwave of Laura’s death. Viewers’ emotional response: One of most popular series ever televised, viewers were glued—not just to the loss of Laura’s cryptic life, but also to the Log Lady, the backwards-talk, the lounge music, the strobe-lit dances, the red velvet and zig-zag floors, and the coffee-and-pie fueled onslaught of ironic Americana.
- Over Tumbled Graves. Jess Walter. 2001. Walter’s jaw-dropping debut humanizes the characters by using multiple points-of-view, including those of sex-workers, criminals, and of course, philosophical detectives. Unlike a lot of serial killer stories, Walter nods toward the banality of the killer’s life and shifts our emotional investment instead toward the lives of the victims, and the messy circumstances that often steered their situations. Readers’ emotional response: empathy for these victims is through the roof. The loss of their lives is a human loss, even on the page. By now, a flipside has clearly emerged in the genre: empathy like this kind of hurts. Some of us may begin to wonder whether we’re reading for entertainment and escape, or to think and to feel—or all of the above?
- Razorblade Tears. S.A. Cosby. 2021. With a level of violence that would make Poe proud, the protags, hellbent on revenge, embark on a quest that entangles them with motorcycle gangs, elitist politicians, and underworld thugs. More important than the raw battles that ensue are the undercurrents of loss these men feel, and the ways they try to change, despite their age, to accept their sons for who they were. Readers’ emotional response: By turns heartbreaking and propulsive, this is another one that conjures our empathy. If these scarred men can grow into acceptance, anyone can.
Sullivan’s point is worth debating. He thinks that today’s crime readers don’t want to be merely entertained. They want to empathize with characters, especially the victims. As a reader, I dislike books wherein the victims are cardboard corpses exploited as plot propellers. As a writer, I work extra hard to bring the dead back to life in readers’ imaginations.
One of my favorite critics was Robert Ebert. He had a great line in his review of Stealing Home, a schmaltzy movie wherein Mark Harmon plays a washed-up baseball player who learns that his childhood sweetheart, Jodie Foster, has committed suicide so he returns to his hometown to fulfill her final wish by taking care of her ashes — and we are treated to flashbacks about their young love. Ebert wrote:
Why has she killed herself? The movie does not supply that sensible question with an answer, and so I will supply one: She killed herself so that she could be cremated and her ashes could be used as a prop in this movie.
Ouch. Two lessons for you: Don’t let your dead person become a prop. Don’t use flashbacks in a feeble attempt to resurrect said prop.
Maybe a definition of “empathy” is useful here, because as I understand it, it’s not exactly the same as sympathy. Sympathy is when you understand someone else’s suffering and feel sorrow or pity for what they are facing. Empathy goes deeper. It’s when you draw upon your own life to relate to another person’s experience or hardship. Example: “I recently lost my spouse so I know what it feels like to feel that deep sorrow and grief.”
This is why empathy in fiction is so powerful and why today’s readers crave it. They want to feel an emotional connection to characters. Even the unlikeable ones. Readers may not like what your character does, but it’s important that you make them understand why they are doing it. This is especially true if you’re working with an anti-hero or morally flexible protag. (think Tony Soprano, Walter White or Harlan Coben’s sociopath vigilante Win Lockwood).
But building empathy for a dead character takes some doing. A big mistake many writers make is assuming that just because a character is dead, readers will automatically feel empathy for them. And often, this manifests itself via the attitude of the protagonist. For me, one of the most irritating tropes in crime fiction is the hyper-masculine dude who plows through the case unscathed and uncaring.
If your protag isn’t feeling anything for the victim, how do you expect your readers to?
So how do you create empathy for your victims? How do you avoid creating cardboard corpses? Treat them like any living character and put flesh on the narrative bones. Some methods I’ve found useful that might work for you:
- Details matter. If you’re wont to create dossiers, make one for your victim. You may not use all the details but it helps you visualize, in your imagination (and thus the reader’s) what kind of person they were. Diaries, journals, photographs, yearbooks, a Facebook page — all are rich fodder. Be careful you don’t make your victim a saint. Make them human.
- What did your victim want? Vonnegut said it might be only a glass of water, but everyone wants something. What your victim wanted might have been what got them killed. You need to know this.
- Connect them to your suspect(s). The most interesting crimes are not random; they are plotted out with purpose and precision. Why did your antagonist choose the victim he did? What details of the victim’s life affected their fate? How did their lives intersect?
- Use other characters. The protag can interview family or friends. Maybe there’s a memorial service for a dead teenager where attendees reminisce. One of the most powerful examples of this is a short story by Tim O’Brien called The Things They Carried. Lieutenant Jimmy Cross, the leader of a platoon of soldiers in Vietnam, carries physical reminders of Martha, the object of his unrequited love. Thoughts of Martha distract Cross leading to a death in the squad. Guilty over his friend’s death and heartbroken, Cross destroys all reminders of Martha so he can focus on the mission. But the theme is that people tell stories about the dead to keep their memory alive. We can’t keep them physically alive in this world, but by remembering them and creating stories about them, we give them another shot at life. You can read the story here.
- Revisit a victim’s physical world. I use this often in my Louis Kincaid books, because Louis feels a strong connection to the dead person when he physically enters their temporal world, be it the bedroom of a teenager girl or the last place they were alive. Culling through a victim’s possessions can be incredibly evocative and emotional, as any of us who has ever had to sort through a relative’s things after a funeral knows.
Let’s give the last word on this to Laura Lippman, in an excerpt from an essay she wrote for the Library of Congress Magazine:
Doesn’t everyone have empathy for victims? I don’t think so. Sympathy, sure. Sympathy is easy. But empathy, true empathy, requires imagining how another person feels. It’s the essential lesson of “To Kill a Mockingbird”; Atticus Finch is constantly exhorting his children to try to see the world from someone else’s perspective.
That novel’s penultimate scene takes place on the porch of the neighborhood weirdo, the reclusive Boo Radley. For years, Atticus’ children have made fun of him, trafficked in gossip about him. But in the end, Boo saves them, quite literally. Scout, who tells the story, stands on Boo’s porch and sees the world as he saw it. “He was real nice,” she tells her father. “Most people are, Scout, when you finally see them,” Atticus says.
Write What You’re Passionate About
It isn’t easy to expose your heart, but the rewards far outweigh the risks. Let me say up-front, there’s nothing wrong with writing to entertain, to allow readers to escape their lives for a while. That’s not what I’m saying at all.
For me, I wanted more. I write to touch lives. I write to make a difference. The latter of which compelled me to write Unnatural Mayhem, my new psychological thriller. The underlying message—the pulse, if you will—strikes at the core of who I am, what I care about, and who I aim to protect. Writing this story required me to peel back even more layers of my heart and soul. I thought, if that’s what I had to do, then so be it. I set out to write a book that matters, a book that could help protect the voiceless, the most innocent among us.
Here’s a snippet:
Imagine a world without animals? No pattering of paws, no wingbeats, no singing in the treetops, no howls at the moon, no buzzing in flower blossoms, no slithering through garden beds, no sympathetic eyes begging for a treat, no unconditional love or companionship, and the oceans, ponds, and lakes devoid of life. The Natural World as we know it would forever be silenced. For eternity.
That passage still kills me, because I can’t even fathom living in a world without animals. I don’t know about you, but that’s not a world I want any part of. Yet here we are, with numerous species on the brink of extinction.
Writing about subject matters you’re passionate about doesn’t mean slamming your reader over the head with your message. Your passion may influence the story, but we must let readers come to their own conclusions in their own time, even if those conclusions differ from ours. Hence why the story needs a compelling plot, or all the passion and heart you infuse into the story won’t make a dang bit of difference.
In Unnatural Mayhem, I focused on the trophy hunting of crows as a starting point for where I’m taking the series. I don’t need to remind you of my undying love for crows, right? Needless to say, the quest shredded my soul, but it also drove my characters through a complicated maze to stop this senseless killing—by any means necessary—before one black feather hit the earth, my passion and their passion intermingled on such a deep, personal level.
Writing about subjects you’re passionate about is also spiritually fulfilling. When I finished Unnatural Mayhem, a wave of accomplishment washed over me, like I’d written the right story at the right time to effect change, and destiny tapped me on the shoulder and said, “Well done.” Like I was always meant to write this story. Like I was always meant to take my Mayhem Series in this direction. Fate.
Have you ever felt this?
Here are a few tips to keep in mind when writing about subjects you’re passionate about:
#1: Find a subject you’re passionate about. Construct the plot around it. Create a cast of characters that would be most affected by it. In my case, I already had the perfect characters to tell this story.
#2: For hot button issues, like trophy hunting and poaching, you need to decide what to show the reader and what to leave out. No one likes dead animals in books. Most of all, me! The trick is to find ways to tiptoe around obvious triggers while still remaining true to the story.
#3: Balance and forethought are key. For every emotional, spiritual, or suspenseful scene, I balanced with some of the most hilarious scenes I’ve ever written. That balance gives the reader time to breathe and makes the book more enjoyable. ARC readers tell me they experienced all the feels, from heartbreak to joy and every emotion in between.
#4: The ending always matters, but it becomes even more important when writing about subjects you’re passionate about. We can’t leave the reader heartbroken. What fun is that? If we leave them uplifted, they’ll look forward to the next book in the series.
#5: When your emotions are tangled up in your characters, let the words just flow. Don’t worry about editing, word choice, or sentence structure. You’re in the zone, emotions spilling on the pages, fingers trying to keep up with your brain. Write first, edit later.
This is my last post of 2022. From my family to yours, Happy Holidays!
 With the fate of the Natural World at stake, can a cat burglar, warrior, and Medicine Man stop trophy hunters before it’s too late?
With the fate of the Natural World at stake, can a cat burglar, warrior, and Medicine Man stop trophy hunters before it’s too late?
Explosive news of a crow hunt rings out in the White Mountain Region of New Hampshire, and one hundred crows gather to put an end to it. With so many lives at stake — including Poe’s — Shawnee and Mayhem must work together to stop the trophy hunters before they obliterate the local murder.
Taking on twenty-five experienced hunters armed with shotguns is no small feat. If they fail, Poe may lead his brethren to their death.
No matter what it takes, this group must be stopped. But what if Shawnee and Mayhem aren’t seeing the full picture? What if these men have secrets worth killing over?
Unnatural Mayhem is on preorder for $1.49. Releases tomorrow (Dec. 13, 2022).
On Abandoned Projects
by James Scott Bell
@jamesscottbell
 I keep all my writing stuff in a dedicated folder on my Mac. I worked really hard to come up with a clever name for this folder. I call it “Writing.”
I keep all my writing stuff in a dedicated folder on my Mac. I worked really hard to come up with a clever name for this folder. I call it “Writing.”
It has many sub-folders in it, absolutely stuffed with half-completed books, stories, ideas, concepts, first lines, clips of news items, and so on.
The other day I traipsed through the folders to see what I was doing ten, fifteen, even twenty years ago. I found several abandoned projects, by which I mean novels I’d made pretty strong headway on yet never finished. Which caused me to reflect on why I might have set them aside.
One reason is that in those early years I was I was writing with reckless abandon. I was coming up with ideas, developing some of them but, for one reason or another, moving on to others. I’m sure you can relate.
So I came across a folder with a title I didn’t remember. In the folder was a document of 15k words, the start of a novel. In another doc in the folder were my notes on same. This project was twelve years old.
I opened the novel and started to read.
Wow, I’m really good! (I humbly thought). I mean, this thing took off like gangbusters. It was laying the foundation for one of those twisty, turny plots that would make Koontz happy and Coben proud.
It has a protagonist who keeps getting a recurring thought of two seemingly unconnected words: Gut bane. Obviously, this indicated a clue his memory wasn’t clear on. Just as obviously, somewhere deep in the plot, the connection would be revealed in time to solve the entire mystery!
I read on, loving myself more and more. At the end of the 15k, the last words written were: Gut bane.
I realized then I could not remember what they meant.
I quickly opened my notes. There I had laid out the basic premise and some notes on characters and scenes.
But not one word on the mystery phrase. Ack!
I did a Mac spotlight search for the phrase. It sent me right back to my abandoned novel-in-progress.
My wail of frustration reached the ears of my editor, the lovely Mrs. B.
“What on earth was that?” she asked.
“The sound of my million-copy bestseller circling the drain!” I said. I explained the situation.
“So why don’t you just make up something new for those words?” she said. She’s the practical one.
“It’s going to drive me nuts,” I said.
She smiled, and I know she was thinking, “You’re a writer, you’re already nuts.”
She is also the wise one.
I have put the Boys in the Basement to work, searching for the ephemeral synapse that holds the answer. But so far, bupkus.
So, note to self (and to you): Don’t ever leave a project without jotting down all the key plot points in that fertile imagination of yours. Even if you jump to something else, you may come back to this one, even years hence.
A few words about process. I’m a plotter, but when I’m in the creative mode, I let myself play. I have fits and starts in my writing folder. I still have a regular “creativity time” where I just let things rip. I play the Title game (make up titles and see what they spark), the First-Line game (boy, have I got some great ones…I just need the novels to go with them), and the old reliable What-if game.
But from now on, I’ll never stop on a project with a great twist without leaving myself a note on what the heck the great twist is!
Duh!
So, do you have abandoned projects of various lengths? Can you remember why you abandon them? Do you plan to go back and restart any?
Weirdness
My reading preferences have changed over the decades. When I first began checking books out from my elementary school library, it was all Cowboy Sam, which evolved to explorers and pioneers like Davy Crockett, Daniel Boone, and Kit Carson.
As a Baby Boomer, my tastes changed when I discovered science fiction and the Gemini Space Program. Then it was Heinlein, Andre Norton, and a host of authors who sent me in search of the stars and worlds beyond our own.
The years passed, and I discovered Texas authors, more old west by Louis L’Amour, Max Brand, and Clay Fischer, then mysteries and thrillers. During college I laid down my change for apocalyptic paperbacks, horror (I’m embarrassed to say I read a lot of John Saul), and fantasy (sword and sorcery).
Suffice it to say, I read what I wanted, and what appealed to me at any particular time in my evolution as a reader. When I finally decided to write that first novel, I honestly didn’t know what it was until three quarters of the way through when I realized it was a historical mystery.
Historical in the sense that the first one took place when I was a kid, back in 1964, which I reckon is history. That reminds me of when I asked the Old Man what it was like back in the Olden Days and the War, and he’d grin and tell me about growing up in the 1930s and fighting in the Pacific Theater, which was then only twenty years in the past.
How’s that for perspective.
So as a published author, I wrote mysteries for a while, before moving on contemporary thrillers set in the west, and now I’m dabbling in westerns. Why?
Well, there was that period in high school when I devoured a host of western authors who reinforced my interest in those old black and white television shows from the late 1950s and well into the 1960s.
But I’ve attempted something different after writing a couple of traditional westerns. I spun off and blended genres, reinforcing that old saw that you don’t chase what’s hot. You write what you want.
I wrote a Weird Western.
What the heck is that!!!???
Thanks for asking.
It’s a throwback to my comic book days, when I absorbed The Rawhide Kid, Weird Western Tales, Weird War, and Western Thrillers. And no, I wasn’t one of those kids that haunted comic book stores, because they didn’t exist as such when I was a kid.
Those comics I collected came off wire racks in the drugstore, or shelves in the grocery store. There was one little bookstore that popped up in our neighborhood around 1968, full of paperbacks by Mickey Spillane and Donald Hamilton, and other authors who would eventually rule the world of hardbacks, like Donald E. Westlake, Joseph Heller, and Kurt Vonnegut.
Back in the corner were the comics and a couple of cast-off chairs that I homesteaded for hours, before finally deciding to plunk down my hard-earned 12 cents for those brightly colored pages that were destined to be mine.
When I got the idea for that weird western, it came in a flash and I hammered it out in six weeks. But now I have this creative, fun, oddball of a manuscript that has yet to find a home.
Oh, I know it will, because I never, ever give up, but publishers are cautious these days, and they work closely with algorithms that reflect sales and public interest. If Idea Number 12493 works, why not publish Idea 12494?
But let’s face it, not every manuscript will see publication. All authors have those first drafts buried deep in a drawer somewhere. I have three secreted away, though one still has potential and some day I’ll dust it off, make the changes that will elevate it above a Drawer Book, and it’ll get out there.
I’m confident there’s a publisher out there who will read my weird western manuscript, leap to his or her feet and shout in appreciation. They’ll likely run around the office, hands in the air bellowing, “Thank you for this innovative work!”
But until then, I’ll keep bringing up this story of a Texas Ranger who dies at the hand of a demented medicine man and is cursed to walk the earth forever with a bit of the Comanche’s dead son lodged in the lawman’s chest.
So with that, here’s an interesting article from the Western Writers of America’s Roundup Magazine about this cross-genre idea. Happy reading!
aug20-weirdwesterns.pdf (westernwriters.org)
