Dutch Post-Impressionism master Vincent Van Gogh was a phenomenal force who helped shape modern art culture. His influence ranks with Shakespeare in literature, Freud in psychology, and The Beatles in music. Van Gogh was also plagued with mental illness, suffered from depression, and was tormented by psychotic episodes.
Conventional history records that Van Gogh died from a self-inflicted gunshot wound in 1890 at the age of 37. However, an independent and objective look at the case facts arrives at an entirely different conclusion—Vincent Van Gogh was actually shot by someone else, and it was deliberately covered up.
 This isn’t to say that Van Gogh was murdered as in an intentional homicide case. As a former police investigator and coroner, I’m well familiar with death classifications. The civilized world has long used a universal death classification system with five categories. They are natural death, accidental death, death caused by wrongful actions by another human being which is a homicide ruling, self-caused death or suicide, and an undetermined death classification when the facts cannot be slotted into one conclusive spot.
This isn’t to say that Van Gogh was murdered as in an intentional homicide case. As a former police investigator and coroner, I’m well familiar with death classifications. The civilized world has long used a universal death classification system with five categories. They are natural death, accidental death, death caused by wrongful actions by another human being which is a homicide ruling, self-caused death or suicide, and an undetermined death classification when the facts cannot be slotted into one conclusive spot.
I’m also familiar with gunshot wounds. Understanding how Vincent Van Gogh’s fatal wound happened is the key to determining if he intentionally shot himself, if he accidentally caused his own death, or if someone else pulled the trigger which killed Van Gogh. Before analyzing what’s known about the Van Gogh case facts, let’s take a quick look at who this truly remarkable man really was.
Vincent Willem Van Gogh was born in 1853 and died on July 29, 1890. During Van Gogh’s life, he produced over 2,000 paintings, drawings, and sketches. He completed most of these in his later years and was in his most-prolific phase when he suddenly died.
Van Gogh didn’t achieve fame or fortune during his life. He passed practically penniless. It was after death when the world discovered his genius and assessed his works of bright colors, bold strokes, and deep insight as some of the finest works ever to appear on the art scene. Today, an original Van Gogh is worth millions—some probably priceless.
Vincent Van Gogh achieved artistic saint status. It’s not just Van Gogh’s unbounded talent that supported his greatness. It’s also the mystique of the man and the martyrdom mushrooming from his untimely death that robbed the world of an artist—a starving artist and a man who lived on the fine line between genius and nut.
Most people know some of Van Gogh’s masterpieces. Wheatfield With Crows may have been his last painting. Café Terrace At Night, The Potato Eaters, Irises, Bedroom In Arles, The Olive Trees, and Vase With Fifteen Sunflowers are extraordinarily famous. So is The Starry Night. (I happen to have a hand-painted oil reproduction of Starry Night right on the wall in front of me as I write this, and my daughter has Café de Nuit hanging in her home.)
Most people know the story of Vincent Van Gogh’s ear. It’s a true story, but the truth is he only cut part of his left ear off with a razor during a difficult episode with his on-again, off-again relationship with painter Paul Gauguin. The story goes on to say that Van Gogh gave the piece of his ear to a brothel lady, then he bandaged himself up and painted one of many self-portraits. I just looked at this portrait (Google makes Dutch Master shopping easy) and was struck by the image of his right side being bandaged. Then I realized Van Gogh painted selfies by looking in a mirror.
And most people know something about Vincent Van Gogh’s time in asylums. This is true, too, and he spent a good while of 1889 in Saint-Remy where he stared down on the town and painted The Starry Night from later memory. The celestial positions are uncannily accurate.

In late 1889, Van Gogh moved to a rooming house in Auvers-sur-Oise near Paris. His painting production went into overdrive, and he was at the peak of his game. On July 27, 1890, Van Gogh left his room with his paints, canvas, and easel. He returned empty-handed with a bullet in his belly.
Vincent Van Gogh’s spirit left this world at 1:30 a.m. on July 29. He passed without medical intervention at his bed, and the medical cause was, most likely, exsanguination or internal bleeding. There was no autopsy, and Van Gogh was buried in a nearby churchyard the next day.
There are various ambiguous statements purported from Van Gogh. He did not admit to shooting himself or intentionally attempting to commit suicide. However, the record indicates he didn’t deny it. The record can also be interpreted that he covered up for someone else.
What is fairly clear is the description of Vincent Van Gogh’s gunshot wound. There are conflicting locations, (chest, stomach, abdomen), but this is explainable from Dutch/French to English translations. It’s highly probable that one bullet entered the left side of Van Gogh’s mid-section and traversed his intestines in a left-to-right direction. There was no exit wound and no serious spinal damage as Van Gogh had walked home from the shooting scene, up the stairs, and to his room where he expired a day and a half later.
There was no firearm found and absolutely no history of Vincent Van Gogh ever owning or operating a gun. He was a painter. Not a hunter or soldier. (Note: There was a rusted revolver found in an Auver field in 1960 which was said to be the weapon. There is no proof that it was.)
There was no suicide note or any deathbed confession. Aside from being an artist, Van Gogh was a prolific writer who documented many thoughts as he progressed from mental sickness to physical health. In late July of 1890, Van Gogh’s writings showed him to be optimistic and with plans to paint as much as possible before an anticipated period of blackness returned. Two days before his death, Van Gogh placed a large art supply order.

Suicide, in Van Gogh’s case, wasn’t surfaced in the early years after his death. There were murmurs among the villagers that “some young boys may have accidentally shot” Van Gogh as he went about his work in a nearby field. There was no coroner’s inquiry or inquest, but there is documentation of a gendarme questioning Van Gogh if he intentionally shot himself to which Van Gogh allegedly replied, “I don’t know.”
The first strong suicide suggestion came in 1956 with Irving Stone’s novel and movie Lust For Life. It was a documentary that took liberty with Van Gogh’s life and times. It concluded Van Gogh was a troubled soul—a beautiful soul—who ended his life intentionally. The book and movie were bestselling blockbusters and cemented the suicide seed to an adorning public.
It became ingrained in lore and public acceptance that Vincent Van Gogh was a desponded psychotic who suddenly up and killed himself rather than continue a tormented existence of interpreting beauty in nature and people. It was the gospel, according to Van Gogh historians, who were comfortable with a suspicious explanation.
Other people weren’t. In 2011, two researchers took a good and hard look into Van Gogh’s life and death. They had full access to the Van Gogh Museum’s archives in Amsterdam and spent enormous time reviewing original material. They found a few things.
One was a 1957 interview with Rene Secretan who knew Van Gogh well. Secretan admitted to being one of the boys spoken about by the villagers who were involved in Van Gogh’s shooting. Rene Secretan, sixteen years old in 1890, told the interviewer he wanted to set the distorted record straight that was misrepresented in the book and movie.
The interview documents Rene Secretan as saying the handgun that shot Van Gogh was his, and that it was prone to accidentally misfiring. Secretan self-servingly denied being present when the accidental shooting happened, claiming he was back in Paris and not at his family’s summer home in Auvers. Secretan failed to identify those directly involved or exactly what circumstances unfolded.
 The researchers, Pulitzer Prize winners Steven Naifeh and Gregory White Smith who co-wrote Van Gogh: The Life, found corroborating statements placing Van Gogh near the Secretan villa on the afternoon of the shooting. They also sourced a leading expert on firearms and gunshot wounds who refuted any chance of Van Gogh being able to discharge a firearm with his own hands that could have caused the wound in its documented location.
The researchers, Pulitzer Prize winners Steven Naifeh and Gregory White Smith who co-wrote Van Gogh: The Life, found corroborating statements placing Van Gogh near the Secretan villa on the afternoon of the shooting. They also sourced a leading expert on firearms and gunshot wounds who refuted any chance of Van Gogh being able to discharge a firearm with his own hands that could have caused the wound in its documented location.
Dr. Vincent Di Maio (a 2012 key witness in the Florida trial of George Zimmerman who shot African-American youth Trayvon Martin in a neighborhood watch altercation) concluded that Van Gogh, who was right-handed, could not possibly have held a firearm as it had to be; therefore the shot had to have been fired by another party. Dr. Di Maio also commented on the lack of reported gunshot residue on Van Gogh’s hands and clothes. In 1890, most cartridges contained black powder which was filthy stuff when burned at close range.
Researchers Naifeh and Smith also took a deep dive into what they could find on Rene Secretan’s background. They painted him as a big kid—a thug and a bully who was well known to have picked on wimpy Van Gogh throughout the month of July 1890. Secretan came from a wealthy Paris family who summered at Auvers with their second home within walking distance of Van Gogh’s rooming house.
According to the researchers of Van Gogh: The Life, Rene Secretan had seen the Buffalo Bill Wild West show in Paris, and Secretan fancied himself as a cowboy character. Secretan fashioned a costume to go with his cocky role of a western gunfighter, and he acquired a revolver that was prone to malfunction. They documented incidents where Secretan would mock Van Gogh as he painted, play pranks on him, and supply alcohol to Van Gogh who couldn’t afford it.
It was during a mocking spat, the researchers surmise, that somehow Secretan’s revolver went off and struck Van Gogh in the abdomen. According to the theory, the boys fled, disposed of the weapon, and formed a pact of silence. If this was true, the question arises of why didn’t Vincent Van Gogh report the truth, and why has the suicide conclusion remained steadfast.
Naifeh and Smith address this in their book with this quote: When all this (accidental shooting theory) began to emerge from our research, a curator at the Van Gogh Museum predicted the fate that would befall such a blasphemy on the Van Gogh gospel. “I think it would be like Vincent to protect the boys and take the ‘accident’ as an unexpected way out of his burdened life,” he agreed in an e-mail. “But I think the biggest problem you’ll find after publishing your theory is that the suicide is more or less printed in the brains of past and present generations and has become a sort of self-evident truth. Vincent’s suicide has become the grand finale of the story of the martyr for art, it’s his crown of thorns.”

As an experienced cop and a coroner, I think Naifeh and Smith are on to something. There are two huge problems with a suicide conclusion in classifying Vincent Van Gogh’s death. One is the lack of an immediate suicide threat. The other is the gunshot nature.
I’ve probably seen fifty or more gunshot suicides. All but one were self-inflicted wounds to the head. The exception was a single case where a shotgun was placed against the chest and the pellets blew apart the heart. I have never seen a suicide where the decedent shot themselves in the gut, and I’ve never heard of one.
Vincent Van Gogh didn’t leave a suicide note. He made no immediate suicide threats and, by all accounts, things were going well for the struggling artist. It makes no sense at all that Van Gogh would head out for a summer’s day, begin to paint, produce a gun from nowhere, shoot himself in the stomach from the most inconceivable position, then make it home—wounded—without finishing himself off with a second shot.
If I were the coroner ruling on Vincent Van Gogh’s death, I’d readily concur the cause of death was slow exsanguination resulting from a single gunshot wound to the abdomen. I’d have a harder time with the classification. Here, I’d have to use a process of elimination from the five categories—natural, homicide, accidental, suicide, or undetermined.
There is no possibility Van Gogh died of natural causes. He was shot, and that is clear. Was he murdered or otherwise shot intentionally? There is no evidence to support an intentional homicide classification. Did the firearm go off accidentally? It certainly could have, and there is information to support that theory but not prove it.
Suicide? Not convincing. The available evidence does not meet the Beckon Test where coroners must establish beyond a reasonable doubt that the decedent intentionally took their own life. If the death circumstances do not fulfill the requirements of the Beckon Test, then a coroner is not entitled to register a suicide classification.
This only leaves undetermined. Coroners hate closing a file with an undetermined classification. It’s like they failed in their investigation.
Unfortunately, in Vincent Van Gogh’s case—from the facts as best as are known—there’s no other conclusion than officially rule “Undetermined”.
I’m no longer a coroner, though, so I’ll stick out my neck.
On the balance of probabilities, I find Vincent Van Gogh was accidentally shot, then sadly died from this unintended and terrible tragedy.
——–
Kill Zoners – Does this theory of Vincent Van Gogh’s death circumstances make sense to you? Have you heard it before? And are you a VVG artwork fan – do his creations speak to you?



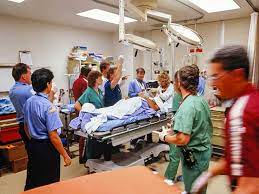 Welch also sniffed the syringe and later agreed with the ammonia-like smell. “It was like how rancid blood smells when people take chemotherapy treatment,” Welch would say. Welch turned the syringe over to Julie Gorchynski, a medical resident, who noticed manila-colored particles floating in the blood as well as confirming the ammonia odor. Dr. Humberto Ochoa, the ER in-charge, also observed the peculiar particles and gave a fourth opinion that the syringe smelled of ammonia.
Welch also sniffed the syringe and later agreed with the ammonia-like smell. “It was like how rancid blood smells when people take chemotherapy treatment,” Welch would say. Welch turned the syringe over to Julie Gorchynski, a medical resident, who noticed manila-colored particles floating in the blood as well as confirming the ammonia odor. Dr. Humberto Ochoa, the ER in-charge, also observed the peculiar particles and gave a fourth opinion that the syringe smelled of ammonia. Taking utter precaution, the backup trauma team sealed Gloria Ramirez’s body in multi-layers of body shrouds, sealed it in an aluminum casket, and placed it in an isolated section of the morgue. Then they activated a specially-trained hazmat team to comb the ER for traces of whatever substance had been released and caused such baffling effects to so many people. They found nothing.
Taking utter precaution, the backup trauma team sealed Gloria Ramirez’s body in multi-layers of body shrouds, sealed it in an aluminum casket, and placed it in an isolated section of the morgue. Then they activated a specially-trained hazmat team to comb the ER for traces of whatever substance had been released and caused such baffling effects to so many people. They found nothing.


 Yes, methylamine is a highly sought-after precursor used in manufacturing methamphetamines. Remember Breaking Bad and the lengths Walt and Jesse go to steal methylamine? Remember the precautions they take in handling methylamine?
Yes, methylamine is a highly sought-after precursor used in manufacturing methamphetamines. Remember Breaking Bad and the lengths Walt and Jesse go to steal methylamine? Remember the precautions they take in handling methylamine? The first responders also succumbed to toxic fumes and had to back off. By the time my cross-shift arrived to view the body, many contaminated people were already at the hospital. My colleague made a wise decision. He signed-off the death as an accident, declined to autopsy, and sent the body straight to the crematorium—accompanied by guys in hazmat suits with the body sealed in a metal container and strapped to a flat deck truck.
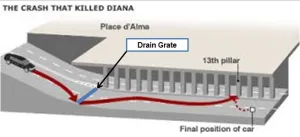
The first responders also succumbed to toxic fumes and had to back off. By the time my cross-shift arrived to view the body, many contaminated people were already at the hospital. My colleague made a wise decision. He signed-off the death as an accident, declined to autopsy, and sent the body straight to the crematorium—accompanied by guys in hazmat suits with the body sealed in a metal container and strapped to a flat deck truck. Circumstances surrounding Diana’s death are exhaustively investigated. Everyone knows basic facts that Diana and her new boyfriend, Dodi al-Fayed, were leaving a Paris hotel for a private apartment and trying to avoid the ever-present Paparazzi. They got in the back seat of a Mercedes sedan driven by Henri Paul—a hotel security agent. Diana’s bodyguard, Trevor Rees-Jones, rode shotgun in the passenger front.
Circumstances surrounding Diana’s death are exhaustively investigated. Everyone knows basic facts that Diana and her new boyfriend, Dodi al-Fayed, were leaving a Paris hotel for a private apartment and trying to avoid the ever-present Paparazzi. They got in the back seat of a Mercedes sedan driven by Henri Paul—a hotel security agent. Diana’s bodyguard, Trevor Rees-Jones, rode shotgun in the passenger front.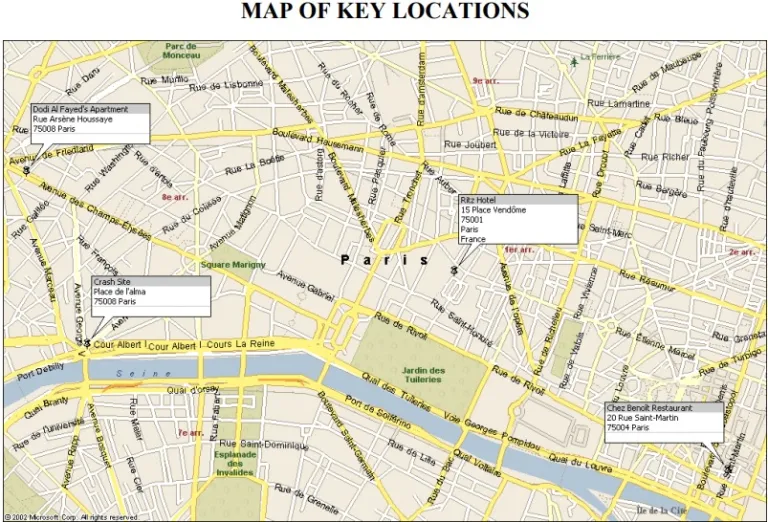
 Blood Alcohol Count (BAC) — 174 milligrams per 100 milliliters of blood or commonly termed a BAC of 0.174% (This was corroborated by his vitreous humor or eye fluid count being 0.173%, his urine being 0.218% and his stomach BAC being 0.191%.)
Blood Alcohol Count (BAC) — 174 milligrams per 100 milliliters of blood or commonly termed a BAC of 0.174% (This was corroborated by his vitreous humor or eye fluid count being 0.173%, his urine being 0.218% and his stomach BAC being 0.191%.)