By Debbie Burke
@burke_writer
In September, my friend Cathy Raven was a featured speaker at the four-day Montana Book Festival in Missoula. Her first book is a nature memoir entitled Fox and I, about her friendship with a wild fox. It won the PEN award, among other honors.
Cathy and I met more than 20 years ago when we took a workshop from Tim Cahill, travel writer and founder of Outside Magazine.
After Cathy moved across the state, we lost touch but recently reconnected via Twitter. On Sunday morning, I drove 120 miles to Missoula for her festival talks and to congratulate her in person.
I’m somewhat acquainted with Missoula so I had an inkling about what was in store.
The streets of Missoula were originally laid out in the 1880s by feuding landowners who each wanted their own hunk of real estate to dominate. Diagonal “Slant Streets” were created for a proposed new town called South Missoula. But political maneuvering stymied the new town and slant streets were surrounded by parallel and perpendicular byways, as shown in this photo. 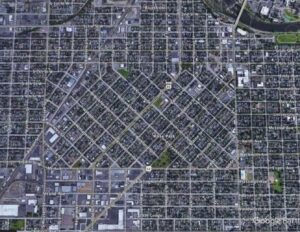
When drivers try to navigate the off-kilter convergence of Brooks Street, Russell Street, and South Avenue, they can thank (or curse) the early citizens who created the notorious Malfunction Junction.
As if diagonal streets and triangle-shaped blocks weren’t confusing enough, routes in Missoula are required to have more than one name—preferably three or four. Brooks Street is also Highway 93 and Highway 12, at least part of the time…until it changes.
Then there’s East and West Broadway. East Alder Street merges with East Spruce Street, which crosses North Second Street East, then eventually runs into West Greenough Drive. Throw in boulevards that are one-way part of the time and two-way other times. Add thoroughfares that dead-end in the Clark Fork River, or at the railroad tracks.
And there you have the mishmash of Missoula.
If Siri had accompanied me, I suspect she would have jumped off the Higgins Street Bridge and drowned herself in the river.
I had printed out several pages of Google maps and have a reasonably good sense of direction. Plus my rearview mirror has a nifty little built-in compass.
I rolled into town about 1 p.m. and missed the motel on Brooks Street because I stayed on 93 which is supposed to be the same as Brooks Street…except when it isn’t.
The Book Festival was at the four-story Missoula Public Library—a skyscraper by Montana standards. While cruising blindly along East Broadway, I happened to spot the towering glass library on the next street over. East Main is a one-way street that amazingly was going the right way.
Success!
Cathy’s phone went to voicemail so I had time to poke around. After the two-plus hour drive, I was glad to climb four flights of stairs to stretch out a bit.
On the top floor, an outside deck around the building featured 360-degree views of the city, rolling hills, and mountains. A volunteer at the book sales table gave me the schedule and, surprisingly, didn’t charge an admission fee, perhaps because it was the afternoon of the festival’s last day.
I peeked into several rooms where presentations were going on but didn’t see Cathy. Back down at street level, I happened to glance over at several people reading at a table.
There was Cathy, deep in her book and writing on a notepad, preparing for her talk.
We hugged like long-lost sisters and visited until she needed to get back to work on her talk.
Her panel was more than an hour later so I figured I’d try again to find my motel.
Missoula is home of the University of Montana. It has winding river walks, bike trails, beautiful historic buildings, and lovely old homes. I know because I saw all of those as I spent the next half-hour totally lost.
The motel was to the south west but, Missoula streets being the way they are, you can’t get there from here.
My mirror compass said I was going the right direction but the street names (aliases, actually) didn’t jibe with Google maps. At last, I found the motel, hiding on a slant street not far from Malfunction Junction.
As I pulled into the parking lot, a woman was getting out of her car, putting a hardback book in her bag.
Turned out she was “Parker,” the evening desk clerk at the motel. We had talked the day before when she made my reservation over the phone.
She said she was an avid reader who spent lots of time at Barnes & Noble.
I told her I was a writer.
That admission is always a bit embarrassing because people’s eyes widen, they smile broadly, and shake your hand as if they’re in the presence of someone important.
We writers know better—the unglamorous reality is we wear sweat pants, sit hunched over computers all day long, play with imaginary friends, and make up stuff. Sane, normal people don’t do that.
Parker took my card, said she loved thrillers, and would look up my books. Cool!
After I checked in, she gave me clear, easy-to-follow directions how to get back to the library. Thanks to Parker, I arrived there in under 10 minutes.
Cathy was on the so-called critter panel—authors who’d written books about wildlife including kingfishers, grizzlies, golden eagles, and Cathy’s Fox and I.
 Despite many awards, stellar reviews, and glowing mentions in Time and People magazines, she’s suffering first-book jitters.
Despite many awards, stellar reviews, and glowing mentions in Time and People magazines, she’s suffering first-book jitters.
Cathy is Mensa-brilliant with a PhD in biology but also shy. She’s much more at home in nature than around people, even though she’s a professor who’s taught hundreds of students over many years.
Her wry, quirky humor quickly won over the audience. Without trying to be funny, she’s very funny.
After the panel, a lot of books by other authors remained on the table but Cathy’s sold out. She fretted about that until I reminded her that selling books was the whole point. Running out meant success.
People mentioned they had ordered multiple copies of her book as gifts.
Her solo talk was an even bigger hit, especially considering it was Sunday evening at 6 p.m. when most festival attendees had already left.
She described her solitary life in the Yellowstone Valley where she’d hand-built her home. As she did research on the area’s botany, weather patterns, and animal behavior, weeks would pass without speaking to another person.
However, a sociable red fox started showing up every day to visit the introverted, reclusive human. They forged an unconventional but close friendship. Trust developed to the point where Fox brought his four kits for Cathy to babysit while he went a distance away to take a nap.
At the end of Cathy’s talk, a woman in the audience presented her with a dazzling sunflower that looked too perfect to be real. But it was.

Dr. Catherine Raven
We headed out for dinner, assured by locals that Missoula has many great restaurants.
Few, however, are open on Sunday night.
For a college town, they roll the streets up early. After a half-hour quest, we found a place, enjoyed a good meal, and had a great catch-up visit.
But, following dinner, we lost our bearings roaming through the dark, deserted downtown and didn’t know how to get back to Cathy’s motel. We drove around looking for a familiar landmark or street name but found none.
Then we spotted a Missoula police cruiser parked alone on a street. I pulled to the curb in front of him and Cathy and I jumped out of the car to ask him directions.
In hindsight, that wasn’t a smart move. But, as a child, I’d always been told if you get lost, ask a policeman.
A young cop jumped out of his rig, talking rapidly into his lapel mic, wearing a wide-eyed deer-in-the-headlights expression. I’m not sure if he had his hand on his weapon because he was standing behind his open car door for cover.
Two women—old enough to be dangerous, from out of town, lost in Missoula, asking directions to a motel whose name we couldn’t remember but was near a McDonald’s—utterly befuddled this poor young cop. I’m sure he thought we were impaired even though we hadn’t had a drop or a toke.
He finally collected his wits (and probably heard back from the dispatcher that there was NOT an APB out on an old white Toyota Highlander with two female occupants). Still looking flummoxed, he managed to direct us to Broadway where we found Mickey D’s and the motel.
Cathy and I said goodbye, resolving not to let another 20 years go by without seeing each other. I headed for my motel on the other side of town.
By this time, I’d driven enough of the mysterious streets of Missoula to be fairly confident of finding my way back until…the southwest section of town went black.
A power outage shut down street lights, buildings, traffic signals, and the sign for the motel. For several blocks, I drove in total darkness except for my headlights. By luck, I spotted the motel just in time to turn into the shadowy parking lot.
In the office, two lanterns glowed. I had a flashlight but, rather than enter a completely black, unfamiliar room, I opted to hang out in the dim lobby with my new friend Parker. A couple of motel workers wearing headlamps checked the property and muttered about buying a generator.
The electric company’s text updates estimated the power would be restored by 9:30 p.m. It was now 9:45. The power had been off long enough that the computer battery backups in the office had run out of juice.
Parker said, before the power went off, she’d looked up my books. She wanted to read them but didn’t have cash with her and I can’t take credit cards.
We spent the next hour, shooting the breeze and solving the world’s problems. She gave me directions to Barnes & Noble, where I planned to go the next morning before heading home.
Finally the lights popped back on.
Whew.
The motel is independently owned, not a chain. Its tagline is “Nice rooms for nice people.”
I went to my room and thought about how nice Parker had been, giving me directions that carried me safely through Malfunction Junction. She’d kept me company during what could have been a nervous hour in an unfamiliar dark place.
I grabbed a copy of Instrument of the Devil (which, fittingly, is about a terrorist targeting the power grid), signed it, and gave it to her.
The next morning, I visited Barnes & Noble. The manager is very supportive of Montana authors, even independently published ones. She ordered a few copies and we talked about my doing a signing there next spring (they’re scheduled months ahead with author appearances).
Despite getting lost repeatedly, inadvertently scaring a cop, and surviving a power outage, the trip to Missoula was a success.
I reconnected with an old friend and watched her bloom as she talked to audiences about her book. I met a lady who gives better directions than Siri and Google Maps combined, whom I hope will become a fan. And I have a future book event to look forward to.
Not a bad day’s work for a writer.
~~~
TKZers: Have you ever gotten hopelessly lost but found a better reward than what you were originally looking for? Please share your wanderings in the comments.
 Decades ago, I was a photography hobbyist. Long enough ago so I was shooting black-and-white film and processing in my home darkroom.
Decades ago, I was a photography hobbyist. Long enough ago so I was shooting black-and-white film and processing in my home darkroom.







 Despite many awards, stellar reviews, and glowing mentions in Time and People magazines, she’s suffering first-book jitters.
Despite many awards, stellar reviews, and glowing mentions in Time and People magazines, she’s suffering first-book jitters.










 George Orwell had his masterpiece, “Animal Farm,” turned down by no less than T. S. Eliot, a big deal at UK publishers Faber and Faber. Like many in the upper echelons of publishing, Eliot missed the point when he rejected Orwell: “Your pigs are far more intelligent than the other animals, and therefore the best qualified to run the farm . . . What was needed (someone might argue) was not more communism but more public-spirited pigs.”
George Orwell had his masterpiece, “Animal Farm,” turned down by no less than T. S. Eliot, a big deal at UK publishers Faber and Faber. Like many in the upper echelons of publishing, Eliot missed the point when he rejected Orwell: “Your pigs are far more intelligent than the other animals, and therefore the best qualified to run the farm . . . What was needed (someone might argue) was not more communism but more public-spirited pigs.” Publishers outdid themselves with boneheaded reasons to reject bestsellers. Conan Doyle’s first Sherlock Holmes novel, “A Study in Scarlet,” was turned down by the prestigious Cornhill magazine because it was too much like the other “shilling shockers” already on the market. The editor said it was too long “and would require an entire issue” – but it was “too short for a single story.” Another publisher sent the manuscript back unread. A third bought the rights for a measly twenty-five pounds, and let it sit around for year. It was published in 1887, and then brought out as a book, but Conan Doyle didn’t get any money from that because he’d sold the rights. Worse, the book was pirated in the U.S. Doyle wrote a couple of historical fiction works. Then an American editor, looking for UK talent, had dinner with Doyle and Oscar Wilde and signed them both up. Wilde wrote “The Picture of Dorian Gray” and Doyle did “The Sign of the Four.”
Publishers outdid themselves with boneheaded reasons to reject bestsellers. Conan Doyle’s first Sherlock Holmes novel, “A Study in Scarlet,” was turned down by the prestigious Cornhill magazine because it was too much like the other “shilling shockers” already on the market. The editor said it was too long “and would require an entire issue” – but it was “too short for a single story.” Another publisher sent the manuscript back unread. A third bought the rights for a measly twenty-five pounds, and let it sit around for year. It was published in 1887, and then brought out as a book, but Conan Doyle didn’t get any money from that because he’d sold the rights. Worse, the book was pirated in the U.S. Doyle wrote a couple of historical fiction works. Then an American editor, looking for UK talent, had dinner with Doyle and Oscar Wilde and signed them both up. Wilde wrote “The Picture of Dorian Gray” and Doyle did “The Sign of the Four.” Kings River Life says “Late for His Own Funeral” is “a fascinating exploration of sex workers, high society, and the ways in which they feed off of one another.” Buy my new Angela Richman, Death Investigator mystery here.
Kings River Life says “Late for His Own Funeral” is “a fascinating exploration of sex workers, high society, and the ways in which they feed off of one another.” Buy my new Angela Richman, Death Investigator mystery here.


