Word of Warning: This is a long, drawn out post of nearly 6,000 words. It’s not that I went to a lot of work today to cook something new. No. Far from it. In fact, I’m really lazy at the moment and decided to regurgitate something I wrote a few years ago when I produced commercial web content articles full-time. Hopefully, this piece I published on my personal blog at DyingWords.net is still relevant and might be useful to other writers & readers who hang around the Kill Zone. BTW, this piece is designed to be scanned, not painfully read word-by-word. Here goes:
——
Web content writing is a different skillset than conventional writing. Most writers are taught to write linearly. We follow a rigid format flowing from basic idea through wordy and detailed exposition, then summarizing with forgone conclusion. I’m guilty of this. Likely you are, too. But it’s not how modern web writing goes.
The internet changed the game. The world wide web impacts every published piece you write. Fortunately, learning how to write effective website content makes you a more practical, productive, and prosperous writer regardless of your niche or genre. And understanding why proper web content writing is different will make you a far better writer in today’s digital world.
 How do I know this will improve your writing? Because for the past 9 months, you haven’t seen much of me around the DyingWords blog. I’ve been busy learning a new skillset. That’s writing content for commercial websites. Working with my daughter, Emily Rodgers and her HealthyContentAgency.com online business, I’ve written over 350,000 words for 279 web content pieces. 87 have been longform articles averaging 2850 words. 192 have been shortforms between 500 and 600 in word count. This experience made me a far better writer.
How do I know this will improve your writing? Because for the past 9 months, you haven’t seen much of me around the DyingWords blog. I’ve been busy learning a new skillset. That’s writing content for commercial websites. Working with my daughter, Emily Rodgers and her HealthyContentAgency.com online business, I’ve written over 350,000 words for 279 web content pieces. 87 have been longform articles averaging 2850 words. 192 have been shortforms between 500 and 600 in word count. This experience made me a far better writer.
I’m a far better writer because I’m forced to economize words and time while being internet friendly. I take foreign concepts (to me) and formulate them into understandable explanations with definite purpose. To get paid, my articles must inform, educate, or entertain readers. Deadlines are strict. Pieces have to deliver value for paying clients. They also have to be found on the internet. That involves accurate research, drafting in a search engine recognition format, and maximizing your proof/ship time. Although commercial web content writing is highly specialized, the techniques are also useful for writing novels and non-fiction.
Web Writing Techniques also Work for Novels and Non-Fiction
Learning web content writing is a large learning curve but definitely pays off. And I know it’ll pay off for you. If you let me show you how, I promise practical information on how to write professional webpage content and blog posts that’ll improve your overall writing skills. That includes purpose, clarity, and—most importantly—your productivity. This translates to pay. It means making money from freelance internet business writing if that’s your interest. Or, you can apply these constructive tips to any of your writings.
 Writing good website content is not the same as producing old-style material for print magazine articles, news pieces, marketing hype, technical documents, or internal memos. Even if you’re already a successful novelist or have numerous publication credits in mainstream journalism, you’ll up your writing game by learning what’s required in producing today’s proper online content material. It’s especially relevant to bloggers and authors who host their own websites.
Writing good website content is not the same as producing old-style material for print magazine articles, news pieces, marketing hype, technical documents, or internal memos. Even if you’re already a successful novelist or have numerous publication credits in mainstream journalism, you’ll up your writing game by learning what’s required in producing today’s proper online content material. It’s especially relevant to bloggers and authors who host their own websites.
Here’s practical advice—not general theory—that’s guaranteed to improve your writing and make you a far better writer.
Understand What Makes Effective Web Content Writing
Web content writing is all about helping people easily understand and retain information on topics they’re actively seeking. It’s also about being found on the net. Good webpages for commercial application are carefully designed to give prospective buyers useful detail about products for sale or information offered. It’s not about direct selling, though.
The idea is to give readers sufficient reason to pursue actions without being pushy. It’s education. Not pure promotion. That might encourage a purchase directly online, visiting a physical retail site, or contacting the vendor directly to acquire a product, service, or information relevant to their needs. It’s also about giving readers a reason to stay on the site, return, and recommend it to others.

Writing effective web content is hard work. It involves three separate sub-skillsets employed in three equal parts.
Research is the first part of developing content. You can expect research to take over one-third of your project time. This is unavoidable as you’ll be given topics you have limited or no personal knowledge about. Then you have to make your words portray intelligent thoughts.
Science is the second part. You need to know how basic technology applies to building an article designed for Search Engine Optimization or SEO. It’s a skill beyond understanding Word or surfing the net. You have to work within Google’s rules of computer science.
Creativity is the third ingredient. You need to put researched material into a clearly readable scientific application that meets client needs. It must be original. It cannot remotely resemble plagiarism as Google will spot that instantly and punish your sins. Besides, your client is paying for fresh content—not cut & paste.
This is as close to a magic formula for web content writing as there is. It’s the combination of factors that resonate with Google, show your work, and let time-pressed readers stay with your article from start to finish. It needs to be relevant, readable, and retrievable. That takes some drilling down to pull off.
Website Content’s Goal is to be Found
There’s far more to effective content writing than setting a hook and reeling a fish. First, your bait has to be found. This is where Google comes in. Understanding how Google works is the key to knowing how to draft, formulate, and execute a web page or post that does its job. That’s to be discovered and convert readers into taking action. Fortunately, there’s not a big mystery around how Google’s search engine works.

Before taking an in-depth look at Google’s operation, let’s review the main elements of properly written web content. “Content” is the term for your combination of words that deliver a message. It also goes further to include everything you do to make a piece internet friendly. Years of writing experience can be good or bad for content writers. I certainly had old habits to break and lots to learn when I branched into building web content. But it’s made me an all-around better writer.
 Good content writing is clear and concise. It’s aimed at a specific audience. Content writing is not the same as “copywriting” or “market writing”. These specialties are hard-sell focused. They’re meant to quickly persuade a defined target market into buying.
Good content writing is clear and concise. It’s aimed at a specific audience. Content writing is not the same as “copywriting” or “market writing”. These specialties are hard-sell focused. They’re meant to quickly persuade a defined target market into buying.
Product descriptions and feature/benefit lists are good examples of copywriting. Content writing takes a softer, rounded approach to conversion. Content writers are good explainers. We take difficult, complex concepts or mundane information and make it digestible.
Think USB — Unique, Specific, Beneficial
The acronym USB in web content writing doesn’t mean your flash drive though it’s sage advice to back your work up. USB is a framework to formulate your content so it works for your audience. Once you know the intent of your piece, you need the information to provide solutions for whoever is reading it.
For instance, you’re likely looking for the solution to being a better writer. That’s why you’re reading this. There’s nothing for sale here. The information’s free. Specifically, I just want to share my unique experience for your benefit.
The best approach in helping others is to make sure all content is:
Unique, where it’s not ripping off other sites. It’s fine to convey the same ideas or general information but it has to dig into sources and be an original presentation.
Specific, where it’s not just a general overview of the topic. Rather, it’s non-general and specifically includes relevant information the reader can use.
Beneficial, where the content has some take-away value. It’s more than just telling the reader. It’s showing them something and allows them to take action.

Content writing is entirely strategic. Before anything is written, content writers develop a series of objectives that form critical goals. This includes a researched understanding of the target market and material specific to the topic. This can be time-consuming. However, it’s crucial to success. It’s specific to the audience and the goals of the client who commissioned your writing the piece.
Before Writing Web Content, You Need to Consider:
Who your target audience is including gender, age range, location, and education.
What the website visitor’s mindset is when they enter the site.
What the audience can learn or achieve from the visit.
What the primary business goal is.
What the secondary business goals are.
 The universal truth of all web users is they require something when they visit a website. They have a need. Your job as a content writer is to fill it. It’s vital—absolutely critical—that content not be written for content’s sake only.
The universal truth of all web users is they require something when they visit a website. They have a need. Your job as a content writer is to fill it. It’s vital—absolutely critical—that content not be written for content’s sake only.
It has to be clear, engaging, understandable, and useful to them. Good webpage content has strategically placed keywords and key phrases but they can’t be so artificially stuffed that they won’t make sense or read smoothly. That’s a turn-off and a sure-fire recipe for click-aways.
Remember, people normally visit websites for one of three reasons:
- Information
- Education
- Entertainment
What you’re doing with content writing is solving problems for people. Knowing your target audience lets you develop the style and breadth your content will take. This is where your personal voice makes a huge difference in setting the tone. It’s like the difference between talking to a bubbly teen and conversing with a pompous Ph.D. It depends on who you’re writing to.
The approach is to be yourself, yet be in tune and respectful with the audience you’re speaking with. It’s also extremely important to consider how internet users or online audiences prefer to read. Internet audiences scan content. They don’t really read.
Consider How Online Audiences Read
Capturing an online reader’s attention is challenging, to say the least. Chartbeat, an internet analytics service, reports that 55 percent of visitors spend fewer than 15 seconds on a webpage before they click away. And Internet Live Stats state there are more than 900 million active websites on the net with 3.5 billion Googles searches done per day.
Getting the right reader to find your content is tough. Having them stick around long enough to absorb your information and then take the desired action is even tougher. We’ll discuss getting them onto your webpage in a bit. Right now, let’s talk about how online audiences read.

The vast majority of internet users don’t actually read webpages. Not in the conventional word-by-word sense that novel or magazine article readers do. Internet readers are conditioned to scan material. Their eyes dart about the page searching for relevant words suggesting links to information they’re after.
This is the main factor that makes web content writing so different from composing and constructing content for printed publications. Google Analytics says that 79 percent of web readers scan instead of closely reading. They skip what they perceive as unnecessary as they’re literally hunting for what they regard as useful. Subconsciously, you’re doing this right now.
Studies repeatedly show scanners take in the first two or three words in a sentence. They ignore the center, then grab the final few words. Scanners do this with paragraphs, as well. But scanners are highly attracted by breaks in information blocks done by imbedded formatting.
Highly Effective Imbedded Formats Appealing to Scanners are:
—Text formatting with bolds, italics and underlining
—Short paragraphs and abrupt sentences
—Word count applicable to subjects
—Highlighted paragraph headers
—H1, h2, h3, h4, heading tags
—Bullet and numbered lists
—Still and video images
—Tables & graphics
—Color variation
—Block quotes
—Whitespace
—Visual flow
—Hyperlinks
Effective content writing is formatted with Google in mind. Don’t think you can trick Google when you’re writing webpage content. This search engine has been around too long and is far too sophisticated for that. You need to understand how to work with Google through Search Engine Optimization or SEO.

The trick is to take SEO principles and work them into your format. You optimize content to get Google’s attention. That means everything you do. Format. Links. Images. Key material. Paragraphs. Sentences. Grammar infractions. Headers. Quotes. Colors. Lists. Bolds. Bullets. Italics. Underlines. Tags. Whitespace. And Words. It’s a holistic concept and it works. All information must be relevant to your topic information. You need to draft it into engaging words that are attractive to Google. It’s the world’s largest search engine and you have to feed Google what it likes.
How Google Finds Attractive Content
They use Googlebots. Ever hear of them? Well, Googlebots have heard of you. Googlebots are probably the most important information invention since the big bang of the internet itself. They’re responsible for making Google a multi-billion dollar international conglomerate.
 Think of the internet as a beach and the web content piece you’re writing as a grain of sand. You need to make your writing grain shine among billions of grains in the sand. You do that by understanding what the Googlebots are looking for and position yourself to be found.
Think of the internet as a beach and the web content piece you’re writing as a grain of sand. You need to make your writing grain shine among billions of grains in the sand. You do that by understanding what the Googlebots are looking for and position yourself to be found.
Search engines like Google constantly look for good content to hit on. That’s the purpose of their existence. They want to help people find what they’re looking for on the web and report it on Search Engine Response Pages or SERPs.
Inserting Key Words and Key Phrases
Googlebots are incredibly sophisticated. They’re able to filter through trillions of information bits and sort what they feel a Googler truly wants. It’s all about determining relevancy to the end user. Google’s search engine does this partly by identifying keywords and key phrases the searcher inputs.
It could be something like writing web content, web writing, how to write effective website content, proper web content writing, writing content for commercial websites, web content pieces, web content writing, how to write professional webpage content and blog posts, improve your overall writing skills, making money from freelance internet business writing, tips on web content writing, writing good website content, proper online content material and practical advice.
Or, it could be any combination of these 27 different keywords that were carefully selected and strategically placed as key phrases in the first 7 paragraphs and 457 words of this article. That’s a total of 62 combined words for a ratio of 1 in 7 or 14% of the opening content being key material and I bet you didn’t recognize the technique on first read. And it’s not “keyword stuffing” because the written content is readable, informative, offers value, and not obviously repetitive.

That’s the difference between artificially-stuffed material that Google passes over and properly written content that Google recommends. If Google senses you’re salting or stuffing key material just for the sake of tricking the search engine into giving your piece a higher SERP rating, it’ll send you to the back of the same bus plagiarism hitched a ride on. You might as well walk than mess up key material.
What are the Best Web Content Keyword and Key Phrase Practices?
—Keys sound best when natural and not “stuffy”
—Make sure keys read naturally for the human audience
—Keys don’t have to be exactly as the best ratings indicate
—Main keys should appear within the first two paragraphs
—Imbed the best key in metadata description
—Keys should appear twice if they don’t seem repetitive
—Use keys in titles and subheadings
—Use variations of keys throughout the content
—Integrate short keywords and longtail key phrases
—Question-based keys are effective but tricky to write
—Question-based keys work best in headings
—Web content keywords and key phrases work well as bullet points
 Don’t make your keywords and key phrases too rigid. “Stop words” are just fine in planning your keys. They’re the filler and connector words like “what”, “are”, “the” & “and” in the preceding subheader question. Google will skip right by them and for good reason. They’re looking for good, readable content and the header “Best Web Content Keyword Phrase Practices” just seems a bit stiff and salted.
Don’t make your keywords and key phrases too rigid. “Stop words” are just fine in planning your keys. They’re the filler and connector words like “what”, “are”, “the” & “and” in the preceding subheader question. Google will skip right by them and for good reason. They’re looking for good, readable content and the header “Best Web Content Keyword Phrase Practices” just seems a bit stiff and salted.
The trick to keywords is carefully researching what your target audience is looking for and what they’re likely going to plug into the search bar. In this case, I’m specifically targeting writers who want to improve their skills by applying techniques used in producing excellent online content. I’m betting that many readers host their own blogs/websites and want to up their traffic.
I’m also doing shameless promotion by adding links to Emily’s HealthyContentAgency.com business and my resources page at DyingWords.net. Don’t be afraid to page through our sites and get tips on writing website content writing. And feel free to follow the hyperlinks to other great web content.
Google Loves Hyperlinks as much as Keywords
Google also loves fresh, original content that has value. Google’s technology is approaching spooky artificial intelligence, and it can instantly recognize a good piece of content that will help the user. It also knows what’s shit, clickbait, and plagiarized. Google’s primary mission is to search the net and be helpful. Hyperlinks from one good site to another are highly helpful as long as they’re staying on the same relative trail.
Hyperlinks or backlinks really unlock the power of the internet. Search engines recognize this information sharing device that you’ve helped them with and will reward you with higher rankings as long as your imbedded links are to other credible content. Links don’t have to be just to written content on websites. Google loves visuals so YouTube links, Instagram, Pinterest, Twitter, Facebook, or whatever site you can work into being relevant is fair game.
 An excellent example of relevant linking is to Google itself. Google AdSense has a thing called Keyword Planner. It a key phrase analyzing tool where you plug in and play with key material you suspect may be best for your content. It’ll give you advice and ratings on what works best according to Google’s search history. Here’s a trade secret. You can also do similar key material searches at Amazon who has the world’s second largest search engine. And a little known but super site is SERPS that works great in rating key words and phrases.
An excellent example of relevant linking is to Google itself. Google AdSense has a thing called Keyword Planner. It a key phrase analyzing tool where you plug in and play with key material you suspect may be best for your content. It’ll give you advice and ratings on what works best according to Google’s search history. Here’s a trade secret. You can also do similar key material searches at Amazon who has the world’s second largest search engine. And a little known but super site is SERPS that works great in rating key words and phrases.
Relevant hyperlinks are a value-added feature in good web content that works to Google’s favor. You’ll increase your overall SERP performance by using valid hyperlinks just as you’ll increase SERP standings by taking a holistic approach to building the entire content in your piece using proper web content techniques. It’s the entire composition that Google assesses and a real case that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.
Googlebots Look at the Total Content Package
Primarily, they love to find information that many people will find useful. Google measures this with a complex algorithm that calculates many details—website visits, page views, lengths of stays, links to other similar content, social media likes—and recommends relevancy of content. It becomes a vicious circle where good content generates large traffic and this cycle grows with Google’s promotion.
Goggle recognizes the entire picture of how web content pieces are formatted. They see and rate formatting, graphics, headers, sentence and paragraph structures, bullets, graphs, whitespace, images, and highlights. Google’s not just looking for a factual read. They’re looking for fun, too. Google knows how internet readers scan, and they want to recommend the best overall reading experience.

And there’s speculation that Google’s becoming a Grammar-Nazi. They’re rating style and substance as well as spelling, grammar, and proper punctuation just like Amazon is now doing when you upload a manuscript. That’s why it’s so important your writing be shipped at the highest standard—a modern internet standard—because Google is watching how you’re optimizing its search engine.
Search Engine Optimization for Google Content
Google’s trade secrets are seriously guarded. Its technology is ever-evolving but generally involves four separate areas that good web content writers need to know. All four should be addressed when drafting a web content page. That applies to all forms of content—short and long form pages, feature articles, static web pages, and even your books.
 Your novels and non-fiction books that are published on Amazon are just as vulnerable to Googlebot sniffing as your own writer website and weekly blog posts. Think of the times you’ve entered a search phrase on Google and how it’s identified an Amazon publication. That’s no accident. The same thing’s going on with your blogs and guest posts, and it’s a fact of life for your author site.
Your novels and non-fiction books that are published on Amazon are just as vulnerable to Googlebot sniffing as your own writer website and weekly blog posts. Think of the times you’ve entered a search phrase on Google and how it’s identified an Amazon publication. That’s no accident. The same thing’s going on with your blogs and guest posts, and it’s a fact of life for your author site.
You can’t hide on the net so the best thing you can do is work with it. That’s the value in understanding how good web content will make you a far better writer. This isn’t new fad or a current trend. It’s a long-tern reality that the internet has changed the way we write to do business. Fortunately, it’s not a hard game to learn how to play.
Four Main SEO Parts for Content Writers to Know
There are 4 main parts in SEO for content writers to know—written, media, tags and authorship. Each one is a separate entity but vital to balance if you want to increase web content exposure and rank high in search results. Let’s look at what each part is.
Written is the core of your internet content writing piece. It’s substance over style every time because Google can’t yet recognize what makes a writer great but it sure tells when writing is bad. A unique voice is desirable but for content it has to deliver information and substance that fits the topic and is helpful. Good content has solid sentence structure, grammar, and sound reasoning. It’s not cutesy and requiring someone to “get it”.
Media refers to visuals. That can be photo images, infographics, illustrations, tables, video, or anything that Google can see. The old saying, “A picture is worth 1,000 words” is so true in boosting your content recognition. Again, it has to be relevant and useful. There are technical tips to know about media insertion such as Alt Tags that briefly define what the picture is. That’s more for the webmaster to worry about, but a content writer needs to be aware of the importance.
Tags go with meta descriptions in getting identified on the web. They also relate to website layout as opposed to content writing. But tags and meta descriptions are hugely important in building an overall effective website or post. The difference between tags and description are tags are visual on the actual piece as it appears on the web and meta description is how it’s presented on SERPs.
Authorship is the authority behind the content. The author’s credentials are attached to the article and give it street creds. The higher profile the content writer has, the better the SEO chance the piece has. An example is my HuffPost profile. I might not get paid for most of these pieces but my SEO ranking is far better because of my authorship on the Huff. Take advantage of every authorship exposure you can. Build a professional profile with a good headshot and link it to every content piece you write. Your SERPs will reward you.

Good Headlines are Highly Important
I’ve found writing effective headlines one of the trickiest parts of content writing—whether for a commissioned client or my own blog posts. There’s an art to this, so I turn to my internet friend Jeff Goins who’s one of the best content writers on the market today. Jeff’s TribeWriters course is excellent value, and he really puts headline writing into perspective.
“Headlines are the first thing people see,” Jeff says. “They need to be attractive, interesting, and descriptive. Headlines should be objective and transform the reader from a browser to being engaged. You need a trigger word such as ‘how’ or ‘why’, a keyword like ‘ways’ or ‘techniques’, a promise like ‘will’ or ‘fix’, and an adjective such as ‘important or quickly’.”
Let’s analyze this blog post’s headline.
“How Web Content Writing Will Make You a Far Better Writer”
Trigger Word — “How”
Keywords — “Web, Content, Writing, Writer”
Promise — “Will Make You”
Adjective — “A Far Better”
Jeff Goins also says there are three basic types of headlines.
World View — “Why Every —— Should ——”
Establish Authority — “What I Know About ——”
Achievement — “ How I ——”
Blogging king Jon Morrow of Smart Blogger has another take on effective headlines in his free pdf download Headline Hacks — A Cheat Sheet For Writing Blog Posts That Go Viral. Jon breaks down good headlines into three simple categories.
The How-To — “How To —— A Million Dollars”
The List — “17 —— To Make Money”
The Bonus — “Get Rich While You ——“
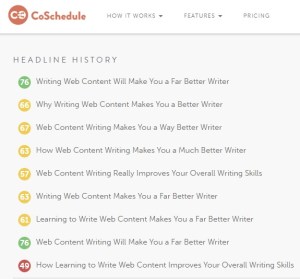 There are excellent web-based headline analyzing tools available. When I was struggling with this blog post’s caption, I threw at least a dozen combinations into CoSchedule and it liked “Web Content Writing Will Make You a Far Better Writer” the best. Check the screenshot image (left) and note how it fits into Jeff Goins’s concept.
There are excellent web-based headline analyzing tools available. When I was struggling with this blog post’s caption, I threw at least a dozen combinations into CoSchedule and it liked “Web Content Writing Will Make You a Far Better Writer” the best. Check the screenshot image (left) and note how it fits into Jeff Goins’s concept.
If you’re handed commercial pieces like Emily administers in HealthyContentAgency.com, you’ll probably have the headlines pre-assigned. That’s good because you can burn up a lot of valuable research, writing, and proofing time struggling for headlines that work. Speaking of researching, writing, and proofing, I’ll show you my actual process that’s let me become proficient in putting out web content pieces at a commercial pace.
First, I’d like to share some general tips for web content writing.
General Tips for Writing Web Content
No doubt there’s a knack to web writing just as there is with every other form of written communication. Top fiction genre writers have their tricks. So do front-line journalists. While these high-profile pen monkeys get their share of glory, there’s not much in it for lowly web scribes. We just put out volume that works on the internet and we stay in the shadows. Most commercial content is ghost-written, anyway.
But there are a number of tips that can help you fine tune web content writing. You can take them over to your own particular brand of wordsmithing. Or, you can leave them as you wish. In no particular order, here are twenty-one content writing ideas I’ve picked up and found to work.

1. Use an active, informal voice. Ditch the passive, formal. Make it personal but not too slick. Find a balance but don’t kill yourself if you use the passive voice, We all speak that way. Being aware is the main thing.
2. Use a mix of short and long sentences. Try not to use more than one conjunction for independent clauses. Yes. There’s nothing wrong with one-word sentences.
3. Use 3-4 sentences per paragraph.
4. Make whitespace your friend. It makes scanning easier.
5. Use a subheading or bold highlight every 5-10 paragraphs.
6. Place keywords in headings and subheadings.
7. Don’t use fancy words. If you need a thesaurus or dictionary, you’re struggling with the wrong word.
8. Write toward a lower-grade audience. I ran the first four paragraphs of this post through the Readability Analyzer app and it rates this content at a Grade 6 reading level. That’s cool!
9. Careful with acronyms. Spell out the entire phrase first, then use the acronym or abbreviation.
10. Work with strong nouns and verbs. Minimize adverbs and adjectives. But not always.
11. Exclamation marks are for 11-year-olds!!!
12. Know grammar rules so when your break ‘em you do so intentionally.
13. You’ll never learn how to properly use commas so don’t sweat it.
14. Invest in The Elements of Style by Strunk & White.
15. Read lots of web articles and blog posts. Learn from the good. Chuck the bad.
16. Never ship work without proofreading. Never. Never. Never. Full stop.
17. Use self-editing tools like Grammarly but there’s no replacing a human eye.
18. Shortform content pieces have their place, but longforms are preferred by Google.
19. Shortforms are between 500-900 words. Longforms are 2300+.
20. Today, a rule of thumb is “the longer, the better”. This post is 5932 words.
21. Always use a Call To Action (CTA) at the end of your content. It’s a must.
Putting Web Content Researching, Writing, and Proofing into Practice
Here’s where the ink hits the page or the images hit the screen in the web writing world. I mentioned that I’ve cranked out over a third of a million commercial web words in three-quarters of a year. That’s not counting all the personal blog posts I’ve written, books I’m working on, and a pile of email messages.
 I’ve worked out a system and recorded some stats that I’d like to share with you. I’m not saying it’s the best way to research, draft, and proof/ship web content pieces. It just works for me and is the best use of time I can make. I also analyzed the last ten pieces and took an average of time spent in each category and how that displays as a time and effort percentage. I’ll show it to you, but first here’s how I put content writing into practice.
I’ve worked out a system and recorded some stats that I’d like to share with you. I’m not saying it’s the best way to research, draft, and proof/ship web content pieces. It just works for me and is the best use of time I can make. I also analyzed the last ten pieces and took an average of time spent in each category and how that displays as a time and effort percentage. I’ll show it to you, but first here’s how I put content writing into practice.
Research
I probably spend too much time researching a topic. But in order to sensibly draft it, I have to understand it. Then the words flow and I can make my words per hour (WPH) cost effective. In other words, it has to return a decent dollar per hour (DPH) because all web content assignments are paid on a flat rate, not by the actual time they take to complete.
I start research by Googling the meat of the topic and see what comes up. For instance, “How To Write Web Content” has 38,800,000 results. That’s a whack of stuff to pour through. Fortunately, Google ranks the best links on the top SERPs so I go from there. (Hmm… I wonder if these content writers intentionally wrote the pieces with SEO in mind to score high rankings…)
Once I find existing content that seems useful, I copy and paste it to a Word.doc and then format it to Ariel 10-point in black on white with 1.15 line spacing and 6-after paragraph spacing. This makes for easy reading and a minimal amount of paper and ink used when printed. I find around 10 articles and stop. Then I print them to hard copy and go over them with a yellow highlighter and a red pen. That’s my code system for identifying pertinent info and facts.
Drafting
Now it’s time to switch hats and start the creative process of drafting the piece. I also switch locations. I do research and reading at home where I have an internet connection but to be time effective, I leave the house and go to the nearby university where I’ve claimed a quiet place in the library. It’s my spot. This change of location changes my mindset. I’m far more productive than at home and not distracted by the phone, door bell, or sneaking peeks at pets on the net.
 I’m nearly twice as efficient at the library. It gets me out and around young, vibrant people as well as being surrounded by thousands of books and millions upon millions of knowledgeable words produced over hundreds of years of researching and writing by some of the brightest minds the world has ever known. Plus, I like it there and it’s quiet.
I’m nearly twice as efficient at the library. It gets me out and around young, vibrant people as well as being surrounded by thousands of books and millions upon millions of knowledgeable words produced over hundreds of years of researching and writing by some of the brightest minds the world has ever known. Plus, I like it there and it’s quiet.
I’m not a fast writer, but I’m clean. I do a bare-bones outline with the introduction, the main points, and the call to action.
Then I start writing. Again, I use Arial font but in 12-point. It’s easier to see on the screen for an old guy like me. The first 500 words are slow and then it takes off. I take a 10-15 minute break once per hour or so, get up, and walk around. This is really important. I rarely go back and review during the draft stage. When the word count for the assignment is reached, I save and go home.
Proofing/Shipping
Now comes the proof/ship phase and it’s quick. I paste the Word.doc into Grammarly and go through it. Grammarly’s great, but it can’t read your mind. Once I catch mistakes like typos, spacing, and bad form, I take the amended Word.doc and change the font to Tahoma 10-point. This proofreading trick really helps to look through a different perspective. Then I scan the document rather than read it word by word. Over the years I’ve developed an ability to speed read. I can accurately cover a 3K word doc in about 10 minutes. And under my breath, I’m reading it out loud.
Once the Word.doc is as clean as I can get it, it’s time to ship. There’s no point beating this thing because it goes to another set of eyes before delivering to the client. I simply ship an email attachment and save it to a folder. Then it’s out of sight, out of mind, and on to the next. I find one longform of around 3K words is enough for one day but it depends on what has to be done and by when.
Something I’ve really learned is how to work within deadlines.
Consistently researching, writing, and shipping within a limited time frame really boosts productivity. It also boosts confidence. That applies to all other forms of writing including my own blog posts and novels. That’s the biggest takeaway I’ve gained from learning how to write web content—applying web content writing principles to novel writing. Overall, it’s made me a far better writer.
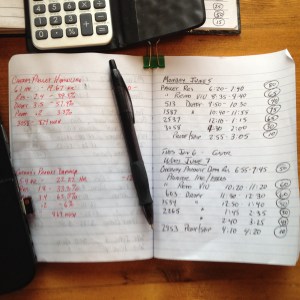 I record exact stats on how my research, draft, and proof/ship time efficiency works out. I carefully record my time into blocks rounded off to 5 minutes. When the piece is shipped, I divide the total time by 60 for an hourly calculation. Then I work it into the percentage of time it took for each phase as well as dividing the total word count (WC) by the actual writing time for the number of words per hour (WPH). I also divide the total project time by the flat fee for the return on overall dollars per hour (DPH).
I record exact stats on how my research, draft, and proof/ship time efficiency works out. I carefully record my time into blocks rounded off to 5 minutes. When the piece is shipped, I divide the total time by 60 for an hourly calculation. Then I work it into the percentage of time it took for each phase as well as dividing the total word count (WC) by the actual writing time for the number of words per hour (WPH). I also divide the total project time by the flat fee for the return on overall dollars per hour (DPH).
Some days production and pay are good. Some days, not so good. That’s how the web content writing business goes. Here are the stats for the average of my last 10 longform assignments.
Total Project Time — 5.83 hr
Total Research Time — 2.0 hr
Average Research Percentage — 36.2%
Total Drafting Time — 3.28 hr
Average Drafting Percentage — 59.3%
Total Proof/Ship Time — 0.25 hr
Average Proof/Ship Percentage — 4.5%
Average Word Count (WC) — 2990
Average Words Per Hour (WPH) — 912
I also keep precise track of the dollar per hour return, but I’m reluctant to share specifics to protect confidential pricing structure. It all depends on the amount charged to a client and how efficient my time is. You can make decent money ($50/hr+) from content writing if you get good assignments and produce quality work fast. Generally, a flat rate will be a set for the article and you can break that down to a certain fraction of a cent per word.

I don’t think I can speed up my drafting time, but I probably do too much researching. However, to cut this down, I probably wouldn’t get sufficient knowledge to write an informative and valuable piece that’d be found on Google. That’s the whole point of the exercise. And it’s why I’m getting paid for web content writing.
I hope you’ve got some decent information and tips on how to write effective web content from this. I sincerely believe it’ll help make you an overall better writer. And here’s the call to action:
Please share this article on social media and email it to friends who’ll benefit.
——
Over to you Kill Zoners. At least the ones who’ve managed to stick with and stay awake in this class. Have you done commercial web content writing? Do you write personal blog posts and web-style pieces? How does this piece relate to your work? And what do you have to share with the rest of us? The floor is open for comments.
——
 Garry Rodgers is a retired homicide detective and coroner who reincarnated as a crime writer and indie publisher. Garry’s based-on-true-crime series are an 8-book run on real cases he worked on (or real cases that worked on him). Now, Garry’s onto a new venture—a hardboiled detective fiction series called City Of Danger.
Garry Rodgers is a retired homicide detective and coroner who reincarnated as a crime writer and indie publisher. Garry’s based-on-true-crime series are an 8-book run on real cases he worked on (or real cases that worked on him). Now, Garry’s onto a new venture—a hardboiled detective fiction series called City Of Danger.
Aside from telling lies on Amazon, Kobo, and Nook, Garry Rodgers is also an old boat skipper with a 60-tonne Marine Captain ticket to prove it. He puts it to use around his home on Vancouver Island in British Columbia on Canada’s west coast.














 How do I know this will improve your writing? Because for the past 9 months, you haven’t seen much of me around the DyingWords blog. I’ve been busy learning a new skillset. That’s writing content for commercial websites. Working with my daughter, Emily Rodgers and her
How do I know this will improve your writing? Because for the past 9 months, you haven’t seen much of me around the DyingWords blog. I’ve been busy learning a new skillset. That’s writing content for commercial websites. Working with my daughter, Emily Rodgers and her  Writing good website content is not the same as producing old-style material for print magazine articles, news pieces, marketing hype, technical documents, or internal memos. Even if you’re already a successful novelist or have numerous publication credits in mainstream journalism, you’ll up your writing game by learning what’s required in producing today’s proper online content material. It’s especially relevant to bloggers and authors who host their own websites.
Writing good website content is not the same as producing old-style material for print magazine articles, news pieces, marketing hype, technical documents, or internal memos. Even if you’re already a successful novelist or have numerous publication credits in mainstream journalism, you’ll up your writing game by learning what’s required in producing today’s proper online content material. It’s especially relevant to bloggers and authors who host their own websites.

 Good content writing is clear and concise. It’s aimed at a specific audience. Content writing is not the same as “copywriting” or “market writing”. These specialties are hard-sell focused. They’re meant to quickly persuade a defined target market into buying.
Good content writing is clear and concise. It’s aimed at a specific audience. Content writing is not the same as “copywriting” or “market writing”. These specialties are hard-sell focused. They’re meant to quickly persuade a defined target market into buying.
 The universal truth of all web users is they require something when they visit a website. They have a need. Your job as a content writer is to fill it. It’s vital—absolutely critical—that content not be written for content’s sake only.
The universal truth of all web users is they require something when they visit a website. They have a need. Your job as a content writer is to fill it. It’s vital—absolutely critical—that content not be written for content’s sake only.

 Think of the internet as a beach and the web content piece you’re writing as a grain of sand. You need to make your writing grain shine among billions of grains in the sand. You do that by understanding what the Googlebots are looking for and position yourself to be found.
Think of the internet as a beach and the web content piece you’re writing as a grain of sand. You need to make your writing grain shine among billions of grains in the sand. You do that by understanding what the Googlebots are looking for and position yourself to be found.
 Don’t make your keywords and key phrases too rigid. “Stop words” are just fine in planning your keys. They’re the filler and connector words like “what”, “are”, “the” & “and” in the preceding subheader question. Google will skip right by them and for good reason. They’re looking for good, readable content and the header “Best Web Content Keyword Phrase Practices” just seems a bit stiff and salted.
Don’t make your keywords and key phrases too rigid. “Stop words” are just fine in planning your keys. They’re the filler and connector words like “what”, “are”, “the” & “and” in the preceding subheader question. Google will skip right by them and for good reason. They’re looking for good, readable content and the header “Best Web Content Keyword Phrase Practices” just seems a bit stiff and salted. An excellent example of relevant linking is to Google itself.
An excellent example of relevant linking is to Google itself. 
 Your novels and non-fiction books that are published on Amazon are just as vulnerable to Googlebot sniffing as your own writer website and weekly blog posts. Think of the times you’ve entered a search phrase on Google and how it’s identified an Amazon publication. That’s no accident. The same thing’s going on with your blogs and guest posts, and it’s a fact of life for your author site.
Your novels and non-fiction books that are published on Amazon are just as vulnerable to Googlebot sniffing as your own writer website and weekly blog posts. Think of the times you’ve entered a search phrase on Google and how it’s identified an Amazon publication. That’s no accident. The same thing’s going on with your blogs and guest posts, and it’s a fact of life for your author site.
 There are excellent web-based headline analyzing tools available. When I was struggling with this blog post’s caption, I threw at least a dozen combinations into
There are excellent web-based headline analyzing tools available. When I was struggling with this blog post’s caption, I threw at least a dozen combinations into 
 I’ve worked out a system and recorded some stats that I’d like to share with you. I’m not saying it’s the best way to research, draft, and proof/ship web content pieces. It just works for me and is the best use of time I can make. I also analyzed the last ten pieces and took an average of time spent in each category and how that displays as a time and effort percentage. I’ll show it to you, but first here’s how I put content writing into practice.
I’ve worked out a system and recorded some stats that I’d like to share with you. I’m not saying it’s the best way to research, draft, and proof/ship web content pieces. It just works for me and is the best use of time I can make. I also analyzed the last ten pieces and took an average of time spent in each category and how that displays as a time and effort percentage. I’ll show it to you, but first here’s how I put content writing into practice. I’m nearly twice as efficient at the library. It gets me out and around young, vibrant people as well as being surrounded by thousands of books and millions upon millions of knowledgeable words produced over hundreds of years of researching and writing by some of the brightest minds the world has ever known. Plus, I like it there and it’s quiet.
I’m nearly twice as efficient at the library. It gets me out and around young, vibrant people as well as being surrounded by thousands of books and millions upon millions of knowledgeable words produced over hundreds of years of researching and writing by some of the brightest minds the world has ever known. Plus, I like it there and it’s quiet. I record exact stats on how my research, draft, and proof/ship time efficiency works out. I carefully record my time into blocks rounded off to 5 minutes. When the piece is shipped, I divide the total time by 60 for an hourly calculation. Then I work it into the percentage of time it took for each phase as well as dividing the total word count (WC) by the actual writing time for the number of words per hour (WPH). I also divide the total project time by the flat fee for the return on overall dollars per hour (DPH).
I record exact stats on how my research, draft, and proof/ship time efficiency works out. I carefully record my time into blocks rounded off to 5 minutes. When the piece is shipped, I divide the total time by 60 for an hourly calculation. Then I work it into the percentage of time it took for each phase as well as dividing the total word count (WC) by the actual writing time for the number of words per hour (WPH). I also divide the total project time by the flat fee for the return on overall dollars per hour (DPH).
 Garry Rodgers is a retired homicide detective and coroner who reincarnated as a crime writer and indie publisher. Garry’s based-on-true-crime series are an 8-book run on real cases he worked on (or real cases that worked on him). Now, Garry’s onto a new venture—a hardboiled detective fiction series called City Of Danger.
Garry Rodgers is a retired homicide detective and coroner who reincarnated as a crime writer and indie publisher. Garry’s based-on-true-crime series are an 8-book run on real cases he worked on (or real cases that worked on him). Now, Garry’s onto a new venture—a hardboiled detective fiction series called City Of Danger.
