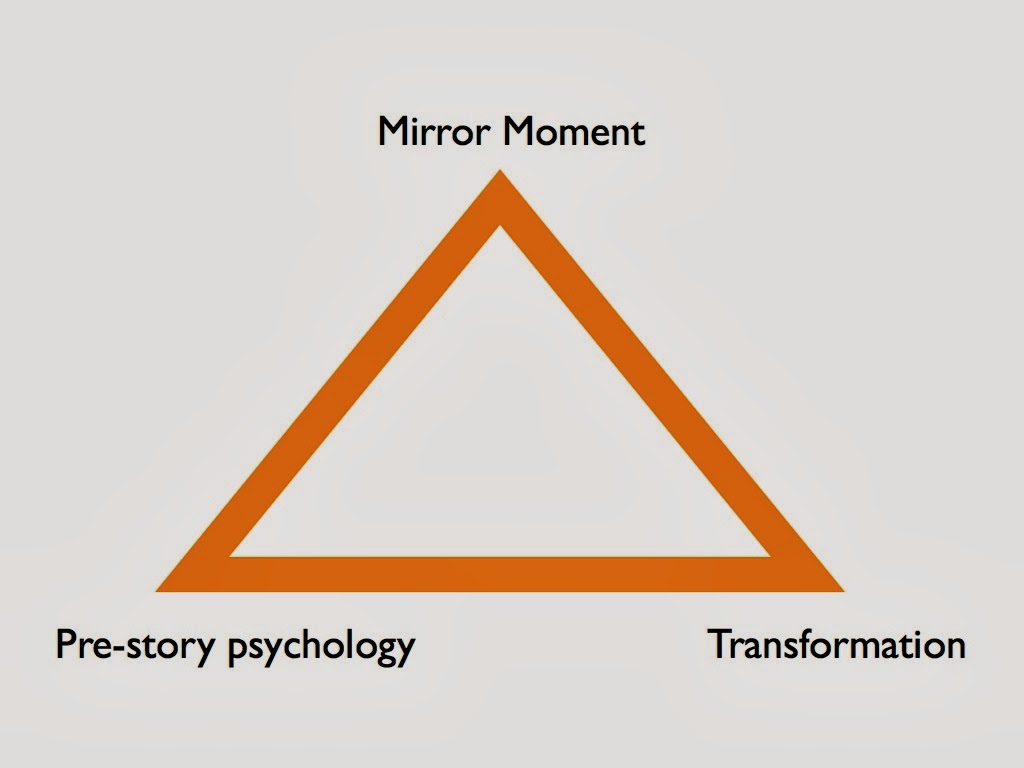
On Monday, guest Steven James had an excellent post on “Fiction Writing Keys for Non-Outliners.” I loved reading his thoughts on trusting the fluidity of the process and chasing after rabbit trails. I can relate to this as a writer. On Tues, our esteemed TKZ contributor, P. J. Parrish, expressed an argument in favor of more structure in her subtle post, “Sometimes You Gotta Suck It Up & Write The Darn Outline” in which she wrote about her love/hate relationship with outlining. These arguments got me thinking about my own process that has evolved over the years.
I started out as a total “pantser,” meaning I came up with a vague notion of characters or a story idea, then started writing to see where it would go. In general, I found this to be liberating and it unleashed my inner story teller, but I found (over time) that I ran out of gas about half way through and hit a wall. I always finished the project. I believe it’s important to finish what you start, if for no other reason than to learn how to get out of tight corners. There’s a true feeling of accomplishment to salvage a story that seemed to be headed for a dead end, and through practice, I learned what pitfalls to avoid. But as a writer under contract, I realized it would be a better use of my time to do some advance thinking on structure, rather than hoisting a shovel to shore up plot holes.
So I found a hybrid method that satisfied my “pantser” free spirit yet provided enough structure to serve as a guidepost – my lighthouse in the fog. I posted a more detailed presentation on TKZ HERE, but I wanted to highlight what this method does for me now.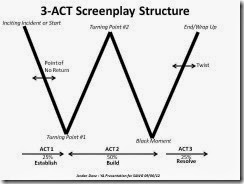
NOTE: A word of caution on any detailed plotting method: A plot structure can become rigid and restrictive if it inhibits the author’s exploration into a new plot twist or character motivation. As Steven James said, some rabbit trails should be explored. For me, this is the fun of storytelling – to uncover a hidden gem of creativity.
When I’m first developing an idea, I break it down into turning points (the 3-Act Screenplay Structure “W”) to get a general notion on structure. It helps me simplify the plotting/outline method into 5 turning points (the W). I can handle 5 things. I use this to write proposals and brainstorm with my crit group for their plots or mine. Rather than getting bogged down by character backstory or other details, I focus on “big ticket” plot movements to provide some substance.
The transition scenes between the turning points are still a mystery that can be explored, but in a synopsis, I can provide enough “meat to the bone” for an editor to get the idea and pair it up with a multi-chapter writing sample. Once I start writing the rest of the book, I can still explore rabbit holes and surprise character motivation twists to embellish the framework I’ve started with. I get my proposal out to my agent (with writing sample, synopsis and pitch) and keep working on current material. While I’m waiting to hear on a sale, I can set the material aside because I have a synopsis to act as a guidepost when I can get back to it. This method has also helped me plot out a whole series, to build onto the storylines (over a series of novels) and ramp up the stakes.
Focusing on turning points from the beginning (before I commit to the writing) has inspired me to spin major plot twists and “play with” the options I should consider. I can reach for complete 180 spins in a “what if” way. As an example of 180 degree turns, I’ve been inspired by the TV show CSI Vegas this season. Many of the episodes are so well written, they make a 180 turn at every commercial break and hit their marks with great twists. I’ve enjoyed this season so much that I record and go back over the plot by taking notes, to see how the writers developed the story. That’s what really good turning points can do for a book/TV show. They pull the reader/viewer into the story and challenge them to figure out where the plot is going. Who dunnit?
So I’m a reformed pantser who has found a way to keep a sense of free spirit, yet write with a framework when I’m ready to go. I feel more efficient, but I still have the flexibility to explore rabbit trails and trust my natural story telling ability.
I’d like to hear from you: How do you handle rabbit trails? Do you put all the work up front in the form of a detailed outline, or do you prefer a lighter touch to “discover” something as you write? Are you a hybrid plotter/outliner too?
Category Archives: plotting
Obstacles, roadblocks and detours
When you write a story, whether it’s short fiction or a novel-length manuscript, there are always two major components to deal with: characters and plot. Combined, they make up the “body” of the story. And of the two, the plot can be thought of as the skeleton while the characters are the meat and muscle.
When it comes to building your plot, nothing should be random or by accident. It may appear random to the reader but every twist and turn of the plot should be significant and move the story to its final conclusion. Every element, whether it deals with a character’s inner or outer being should contribute to furthering the story.
In order to determine the significance of each element, always ask why. Why does he look or dress that way? Why did she say or react in that manner? Why does the action take place in this particular location as opposed to that setting? If you ask why, and don’t get a convincing answer, delete or change the element. Every word, every sentence, every detail must matter. If they don’t, and there’s a chance they could confuse the reader or get in the way of the story, change or delete.
Your plot should grow out of the obstructions placed in the character’s path. What is causing the protagonist to stand up for his beliefs? What is motivating her to fight for survival? That’s what makes up the critical points of the plot—those obstacles placed in the path of your characters.
Be careful of overreaction; a character acting or reacting beyond the belief model you’ve built in your reader’s mind. There’s nothing wrong with placing an ordinary person in an extraordinary situation—that’s what great stories are made from. But you must build your character in such a manner that his actions and reactions to each plot point are plausible. Push the character, but keep them in the realm of reality. A man who has never been in an airplane cannot be expected to fly a passenger plane. But a private pilot who has flown small planes could be able to fly a large passenger plane and possibly land it under the right conditions. The actions and the obstacles can be thrilling, but must be believable.
Avoid melodrama in your plot—the actions of a character without believable motivation. Action for the sake of action is empty and two-dimensional. Each character should have a pressing agenda from which the plot unfolds. That agenda is what motivates their actions. The reader should care about the individual’s agenda, but what’s more important is that the reader believes the characters care about their own agendas. And as each character pursues his or her agenda, they should periodically face roadblocks and never quite get everything they want. The protagonist should always stand in the way of the antagonist, and vice versa.
Another plot tripwire to avoid is deus ex machina (god from the machine) whereby a previously unsolvable problem is suddenly overcome by a contrived element: the sudden introduction of a new character or device. Doing so is cheap writing and you run the risk of losing your reader. Instead, use foreshadowing to place elements into the plot that, if added up, will present a believable solution to the problem. The character may have to work hard at it, but in the end, the reader will accept it as plausible.
Always consider your plot as a series of opportunities for your character to reveal his or her true self. The plot should offer the character a chance to be better (or worse in the case of the antagonist) than they were in the beginning. The opportunities manifest themselves in the form of obstacles, roadblocks and detours. If the path was straight and level with smooth sailing, it would be dull and boring. Give your characters a chance to shine. Let them grow and develop by building a strong skeleton on which to flesh out their true selves.
Discovering Story
Part of the creative process is Discovery. I’m in this phase now, which is when the beginning of a plot swirls in my head. I have a title for my next mystery, so I have to work the murder around it. Thus I’ve made an appointment for a facial. I know, research can be tough but someone’s got to do it. And my Bad Hair Day series is centered around a beauty salon.
Often I’ll start the plotting process with the victim. As shown in my book, Writing the Cozy Mystery, I draw a circle in the center of a paper and put the victim’s name inside. Around that go spokes like on a wheel for each of the suspects. Then I connect the spokes together so it becomes more like a spider’s web, where the suspects relate to each other in some manner.
For now, I know my victim’s basic identity. Her job is what gets her into trouble, and so the suspects develop from among her business associates. Who might want her dead and why leads me to motives. At this point, preliminary research is in order. I need to look up the world surrounding her business and learn more about it.
But that’s not all. I am driven to acquire new knowledge about a subject for each book. What will it be for this one? What issue interests me, or what news article have I filed among my clippings that I might want to pursue? This factor is what propels me forward and underlies the plot. It hasn’t come to me yet for this story.
My victim is co-sponsor of a beauty pageant. I search online and fine headlines like “Top 10 Beauty Pageant Scandals.” Bingo! Before looking these over, I realize I have a problem. Most pageants likely take place over a weekend. How can I get this group of people to stay in the Fort Lauderdale area for a week or two so my hairdresser sleuth, hired to do the contestants’ hairstyles, can ferret out clues?
I’ll deal with that problem later. Meanwhile, I look at the scandals online regarding beauty shows, and nothing strikes me in terms of issues I’d want to pursue. The problems encountered don’t seem worthy of murder. And do I really want to write a whodunit variation of Miss Congeniality?
Hey, what if I do a fashion show instead of a beauty pageant? My last Bad Hair Day mystery, Peril by Ponytail, takes place in October. I could set the new story in December. I’ve done Thanksgiving in Dead Roots but never Hanukah or Christmas. So how about a charity holiday ball with a fashion show? Using a local designer would keep the action in town, and I’ve already done the preliminary research by going backstage at a designer showcase. This will give me the personal angle of Marla and Dalton dealing with the holidays while also picking a charity whose cause I can support. If Marla has a connection to the charitable organization through her friends or relatives, this would give her an added incentive to get involved in solving the murder.
I like this idea. It’s starting to get me excited, whether or not it pans out. At least, it’s a start in the right direction.
So what advice do I have for you based on this experience? When you begin to think about the next story, let ideas flow through your brain. Pick the one that excites you and do your preliminary research. If you find some meaty material, go with it. If not, let the idea float away but keep the story in your mind. Your subconscious will present the next idea. Or thumb through your files and see if one of your clippings or news pieces stimulates a train of thought.
Do you start story development with an issue, a character, or a setting?
A New Approach for Plotters, Pantsers, and Everyone in Between
Story Logic
The other night, I watched two recorded TV action adventure shows that gave me pause over their story logic. If I had written these sequences into a book, editors everywhere would have turned down my submission. What was wrong? Flaws in story logic jumped out at me. Whether the average viewer noticed, I have no idea. But as a storyteller myself, I couldn’t help but make note of them.
In Show Number One, two female characters were attempting to steal a precious artifact from a security-tight room. They got around the fingerprint analysis in a plausible manner and entered the vault-like space where the artifact was kept under a glass case and surrounded by an electrified cage. Various obstacles were placed between the door and the cage. But wait—one of these woman was an acrobat specifically chosen for this impossible task. So she vaults up to a series of parallel bars conveniently strung across the room and swings from one to the next, while her pal waits by the door. Finally, our acrobat propels herself over a gap at the top of the electrified cage. Inside, she swipes the artifact. Guards are moments away from discovering them. Commercial break.
When we return, the thieves are outside with their booty. Okay, how did they get from Point A to Point B? When we saw our acrobat in action, she used her two hands to swing and jump from one overhead bar to the next. How could she jump at all holding the heavy, bulky artifact that looked as though it would require those same two hands to hold it? Illogical. Nor did she have her friend present again to give her a boost up.
My editor would have caught me on that one. My solution? Have her wear a backpack so she could stuff the heavy tome inside for the return trip. Give her a tensile line to shoot to the overhead bar from inside the cage. Or have her rappel down from a ceiling vent like in countless heist movies. Don’t just have the two women suddenly appear in the clear with their prize with no explanation as to how they got away and avoided the guards.
Story Number Two proceeded well until the very end, when a bad guy got his comeuppance. One of the main characters called him on his cell phone as he’s in the bathtub with a beautiful woman. The caller mentions how his turn has come right before his companion stabs him. How did this character know exactly when he’d be in the bathtub with the assassin? If it were my story, I’d have video cameras tracking him. Or the assassin could have sent the caller a signal. It was too much of a coincidence that this person called right then, although the dramatic moment worked to provide a sense of justice.
What does this prove? TV writers might get away with flaws in their story logic, but it won’t work for us when we’re under an editor’s eagle eye.
Make sure your story flows logically and smoothly, covering all bases. You don’t want to give your readers cause to put down your book with a derisive snort.
Do you recall any movies or TV shows where the credibility stretched?
Key Elements to Writing an Effective Synopsis
Jordan Dane
@JordanDane
 |
| He’s flummoxed because these aren’t his hands. |
I don’t know of any author who hasn’t been flummoxed (word of the day courtesy of James Scott Bell) by the task of writing a first synopsis. Do they get any easier to write? Not for me. Each story idea presents a unique essence that must be distilled into a short brief. Some authors sell books on proposal (with or without a writing sample), or they use the synopsis to be an initial outline of the story idea (a guide post), or an effective synopsis brief can be a part of a solid query letter or made into a quick pitch to an editor or agent. However you use a synopsis, I thought I’d share what has worked for me.
Key Elements to Writing an Effective Synopsis
1.) The Basics – Generally a synopsis is 5-7 pages long, double spaced with one-inch margins. Be sure to include your contact information on the first page and I would recommend adding a header on every page (in case an editor or agent drops your proposal and the pages get out of order). My headers have my name, title of the book, genre, word count, and page number (on far right). I often have a tag line that I list at the top, before the synopsis brief. If you are represented by an agent, I would list that near your contact information. A professional presentation will make you stand out in a slush pile.
2.) Writing a synopsis shouldn’t be about defining the rules of the game. It should be about why you’d want to PLAY it. Give the editor or agent or reader a sense of your voice and the color of the world you will build. Think of a synopsis as a lure, an enticement for them to want more. Rules are boring. Tell me why the game will be really good, or fun or scary.
3.) Whether there is quirky humor or a dark suspenseful undertone to your book, the synopsis should reflect these elements and not merely be a detailed “who does what where.” If your synopsis is boring, chances are any editor or agent will think your book will be lackluster, too. Give them something shiny to grab at.
4.) Pitch your book with a high-level synopsis brief at the top of your proposal. This pitch should read like a TV log line – a condensed 1-3 sentences about the main elements of your story – character highpoints, conflict, emotion, what’s at stake. No need for specific character names that will only be a distraction to what your book is about. If you get this short pitch right (sometimes called the “elevator pitch”), you can embed it into a query letter or use it on your website for a short teaser. An editor can use this short descriptive pitch of your book to her house and the committee that decides which book to buy.
EXAMPLE:
[Part of this pitch is omitted for confidentiality. I REALLY wish I could share it, but I can’t.]
A depressed and aging widow gets a second wind when she pays a young handyman for services rendered on her unusual Bucket List, in an uncommon “coming of age” story.
5.) After the synopsis brief or the pitch, it’s time to introduce your characters. The first time a new name appears in your synopsis, capitalize their full name to highlight who the players will be. A writing sample will introduce your character to the editor or agent in a different way, but I recommend a brief summary of why each of your main characters have earned their right to be a star in your story. Highlight who they are, what they want, and why they can’t have it. What will their struggle be? What’s at stake for them?
EXAMPLE:
LILLIAN OVERSTREET has flipped the channel on her rerun life and given up. She’s convinced nothing exciting will ever happen to her. Her husband’s dead, her only daughter treats her like a doormat, and old age is creeping up on her like bad granny panties and has made her invisible. Her only reason to leave the house is her bowling team of widows – The Ball Busters. She’s mired in a chronic case of depression that has seeped into every aspect of her existence, until her daughter GRACE OVERSTREET-THORNDYKE hires “eye candy” to do the renovation of the family home. [This is only the basic set up and does not include the conflict, black moment, and ending highlights.]
6.) Not every aspect of your plot needs to be spelled out, ad nauseam. If there are five main suspects or key secondary characters, give the highlights of who they are and why they earned the right to be in your book and why they could be a game changer. This works for other genres, not just crime fiction. If there are characters who stand in the way of your hero/heroine, showcase who they are and why they are an obstacle.
EXAMPLES (Secondary Characters with sense of color/humor):
VINNIE DELVECCHIO is the only widower on the Ball Busters team. In the small town of Why, Texas, he runs a Deli where Lillian gets her meat. He’s opinionated and brash with a foul mouth. He teases the ladies at the bowling alley by saying, “If you gals ever need someone to slip you the sausage, you come to DelVecchio for quality meat.” Even though his mind is constantly in the gutter, Vinnie knows how to roll a strike, has his own bowling shoes and a hefty pair of designer balls, but he’s only on a “team of broads” for the view.
CANDACE and VICTORIA WINDGATE are twin sisters Lillian has known since high school. The sisters kept their maiden name after both their husbands died in the same mysterious boating accident. No one in town knows how the Windgate twins earned their financial independence or how much money they have, but rumors never run out of steam in Why, Texas. Neither of the sisters can bowl worth a damn. They only come to ‘Why Bowl – Family Center & Tanning Spa’ for the cheese fries and beer.
7.) The major plot movements should be highlighted so an editor or agent will know your story has meat to the bone. I like to use a 3-Act screenplay method and have posted about it at TKZ before at this LINK – I use a big “W” to remind me of the turning points to include in my synopsis. (Michael Hauge’s “Writing Screenplays That Sell” was the reference book that sparked my interest in structure and it has helped me draft my proposals.) The highpoints should show the stakes ramping up and the key turning points in the plot as well as the black moment when all seems lost. If there are twists in the plot (especially surprises), showcase those too.
Key Questions for a 3-Act ‘”W” structure:
Act 1 – How does your book start?
Act 1 – What is the point of no return for your character(s)?
Act 1 – What key plot twist will propel your story into the escalation mode of Act 2?
Act 2 – How will you up the stakes?
Act 2 – What is the black moment when all seems lost for your character(s) and how will your character(s) turn it around?
Act 3 – Do I have a plot twist for my readers?
Act 3 – How will your story end and how will you tie up the pieces?
8.) The ending should be spelled out. Editors and agents don’t like surprises and want to know how you intend to tie things up. If you are writing a romance, the ending is very important so the editor or agent gets a feel for your take on a romantic full circle. I’ve sold books without full disclosure of who the bad guy is, but generally you should “tell all.”
Even if you are an indie author and may never have written a synopsis or included one in a proposal to an editor or agent, it can be a good exercise to understand the essence of your book. A good synopsis will get you thinking about how to create an effective jacket cover description to entice the reader. Writing a synopsis is always a challenge, even if you are good at it, because it boils down your book into a teaser that you hope will lure a reader to buy your book.
For the purpose of discussion, tell us what works for you in writing a synopsis. (If you have any tips to add, please share them.) Or share what challenges you’ve had. Let’s talk, people.
What Makes a Critique Group Work?
Yesterday I attended the first meeting of my new critique group, the first group I’ve been in since 2004. I’ve never had much luck with such groups, probably because I was so new to writing that I didn’t know what to even want from a group. I had even started one and had to drop out, but this time should be different.
There are four of us. Very experienced authors. We have a mix of genres, which could make things interesting. I wasn’t sure how well I would fit in. I’m the only crime fiction and YA writer, but after our meeting and the fun we had brainstorming plots, it became apparent very quickly that genres won’t matter. Storytellers know how to kick start a plot.
 |
| Texas Hill Country Bluebonnets |
We met in the beautiful hill country of Texas, outside Boerne. Gorgeous drive up to a member’s beautiful home. The scenic drive is enough to start the creative juices flowing. Our hostess had lunch prepared, something easy and way too yummy. She knew the other two authors and had gotten us together after I whined about not finding what I needed in a few of my local (larger) writers’ groups.
We chatted via email on what we’d like to get from our group. At first I wasn’t sure my goals would match up. Initially we had planned on meeting once a month to talk about the business of writing and maybe brainstorm on plot or scene issues, but after the meeting yesterday, we are getting together once a week and it will be much more on craft and pushing each other to be the best we can be.
Yes, we talked promotion and I learned some new things there and we shared contact info for promo things that worked for each of us. We chatted about plotting methods and storyboarding, but when we got to brainstorming a plot, that’s where my mind was blown.
One of our members had purchased three covers from a designer, images that spoke to her. None of us realized what her intentions were until we got into it, but she bought the covers BEFORE even knowing what any of the books would be about. Basically our session turned into a major Flash Fiction exercise of brainstorming what a new series would be about using the cover designs for books that didn’t exist. HA! When you get the right people together, the ideas flow and we had a blast doing it. We set the stage for a world she’d be building from those three covers that would be bigger than three books, something she could grow into. I’d never done that before and I can’t say I would recommend it as a method of plotting, but with the right people, you never know where things will go.
So we set up our basic crit group intentions as follows:
1.) We will endeavor to get together weekly and bring new material from our current projects. The author will read (& hand out copies of the material), but advance copies will be made available to the other members prior to our meeting for “track changes” feedback. This will allow us to focus on the reading.
2.) None of us are very interested in line edits (unless something is glaring), but we want to get feedback on character, plot, scene choice, motivations, etc. (Craft issues)
3.) We will help each other through plot glitches and even do a “getaway retreat” for serious plotting sessions on future books.
4.) We chatted about limiting our reads to a number of pages and/or a time limit per member, but none of us liked the rigidity. So as we get into this, we will be considerate of not overstepping each other’s time and bring what we need to read to keep us on any publisher’s deadline. We will stay until everyone gets what they need.
5.) We’ll rotate the meetings between member’s houses, as long as the commute isn’t too much on any one person. (Two authors are located more conveniently for all of us.)
6.) We are at four members and like that headcount. Whatever we say in the group will be confidential.
So that is a summary of my new crit group. I’m sure we will define things as we go, to suit the needs of the group, but I’d love to hear from you, TKZers.
For discussion purposes, my questions to all of you (who have way more experience than I do with critique groups) are:
1.) What works in your groups? What do you look for in a crit group?
2.) What doesn’t work?
3.) What do you wish you could add to your groups?
Jordan Dane’s Crystal Fire (The Hunted Series with HarlequinTeen) now available for pre-order. Release November 26, 2013.
“The Hunted – Strong characters and a wild and intense story.”
4.5 Stars – Romantic Times Magazine
Plotting visually:You’ve got to see it to believe it
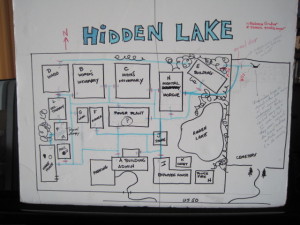
One of the biggest problems I think many manuscripts have is that the reader can’t VISUALIZE the physical action ie the moving around in physical space of the characters. Because the writer has not done an adequate job of describing places and actions, we are confused. And maybe it’s simply because the writer did not take the time to “draw” things out in his own mind. It’s important that a writer be able to clearly SEE a story so that the reader can as well.
Bingo. Once I drew it, I realized I had everything wrong, including what side of the highway they were on.
What about you guys? I know we’ve got pantsers and plotters out there. Any picture makers? Send me your examples and we’ll do a follow up. Send them to killzoneblog at gmail dot com. (Sorry, gotta spell it out to avoid spammers) Show me your pictures!
Keeping a Dirt File
For mystery writers, having a dirt file is akin to keeping a gold mine in your house. What is it? I’m referring to a folder full of clippings you’ve taken from the newspaper or magazines that may be relevant to your work someday. I get out a pair of scissors whenever I read a paper copy of the Sunday newspaper. A recent issue’s headline caught my eye: Bomb Case Awash in Mystery. 
As soon as I saw mention of a pipe bomb found under an SUV in a suburban neighborhood, I knew I’d hit gold. Suspect A noticed something strange under his car. It turned out to be a homemade bomb. He accused his wife’s lover of planting the device. This man, suspect B, said that he was framed by Suspect A and the wife. But it didn’t help his claim of innocence when the wife was found to have a $500,000 life insurance policy on her husband. Then the lover’s DNA was found on the bomb. But was it rigged to go off, or was it set as a false trail? To complicate the issue, police discovered videos of Suspect B and his stepdaughter having sex. Oh, man. I couldn’t have made this up! You know how truth is stranger than fiction? Here’s a perfect example.
When might I use this information? When I’m determining the suspects in my next mystery. I’m always looking for motives and secrets people may hide. Or an article like this might kick off a new plot. Think about the puzzles here. It seems an open-and-shut case about the wife and her lover trying to do away with the husband. But what if it’s really the husband and wife trying to frame the lover? Why would they do that? What if…? And here we go. Our imagination is off and running.
Stockpiling clippings doesn’t only apply to the mystery genre. For my science fiction romances, I obtain articles on futuristic technology, whether it’s on flying cars or electromagnetic weapons. Even the power of invisibility has a basis in reality. I have articles to show for these topics. I also cut out stories of true adventure travel. You never know when my hero might have to explore a volcanic crater or traipse through a jungle. Even off the beat pieces that tickle my fancy go into a general research file. You might need inspiration and one of these printouts could fire your imagination.
So are you a crazy clipper like me? I make sure my husband reads the newspaper first before I put holes in it. What kind of dirt do you look for?
Cornered
Have you ever written yourself into a corner? Have you progressed at least midway through your story and then realized your hero is going down a black hole and you don’t know how to get him out?Recently, I found myself in this situation. In my synopsis, which acts as my writing guideline, I was up to the part where the hero, Lord Magnor, goes to the underworld to obtain a sacred book stolen by Hel, Queen of the Shades. To get there, he has to die. Circumstances with the heroine make him despair of their future together, and so he takes a poison pill that another character has given him.
Here is what my synopsis said:
He awakens underground in front of an iron gate. This leads to a gold-paved bridge that crosses the river Gjoll. Beyond is Helheim, where Hel resides. A giantess guards the gate and asks him for the password. If he fails to give the right answer, she’ll toss him in the river and it will carry him to the land of fire and eternal torment.
Magnor figures out a way past and meets Hel. She isn’t willing to give up the Book of Odin, not even for the mead he’s brought. So he creates a diversion and steals the sacred book.
Now this presented several problems. How does he get past the giantess when he fails to give the right password? How does he get into Hel’s palace? What kind of diversion does he create, and how does he steal the ancient relic?
I printed out these questions and sat on my “thinking couch” until the answers came to me. First of all, if he fails to give the right password, the giantess won’t throw him in the river. Instead, she’ll doom him to spend eternity in the company of other lost souls.
At that point, he has to find another way past the gate. He doesn’t have any cutting tools or acid to break in at some point farther down the line. And even if he could do so, how would he cross the raging river? What he does have are his wits, so he eases into the shadows and cheats by climbing up the rocky wall lining the chamber and gaining access to the opposite bank that way. In other words, he goes up and over instead of across. It’s the Kobayashi Maru solution from Star Trek. If you’re in a no win situation, change the rules.
So what about confronting Hel? He decides upon a frontal approach, stating his business to the palace guards in such a confident manner that he convinces them to allow him an audience with the queen. I’m glossing over the details but suffice it to say he states his case to her and she refuses to comply. Now we need a distraction so he can steal the book that rests in a glass case.
In the story, I’ve already planted the seeds for this solution. He’s been given a magic horn that is supposed to sound a warning when the demon, Loki, is near. But what will happen if Magnor blows the horn within Hel’s palace? He does so, and glass shatters throughout the hall, including the case protecting the sacred book. He snatches the artifact as Hel’s minions surround him.
Now what? The heroine has been told she must obtain a golden apple from the Fae to revive him. But fairies aren’t part of Norse mythology, which my story is based on. Here is what my synopsis says:
Erika must return him to the land of the living. She realizes how much he means to her and won’t risk losing him. However, reviving him isn’t easy. Aware that she only has a certain window in which to resuscitate the warrior, she saves him just in time.
Okay, how does she save him? Anytime you leave things vague like this in your synopsis or writing outline, eventually you have to come up with the details. Again, I’d already sowed the seeds within the story. Erika, a descendant of Odin, has inherited some of his shapeshifter powers. She cannot change her own form, but she possesses the power to manipulate the earth.
Odin also had the “breath of inspiration”, and this reminded me of the breath of life possessed by the Mord Sith in Terry Goodkind’s Sword of Truth series. What if, instead of going to the Fae, Erika is inspired by the figurines of fairies she’s designed in her pottery studio? Fairies might not be real, but what about fairy dust? And so she uses her innate power to revitalize the hero with the magical dust she breathes into his mouth.
As you can see, whatever corner you back your hero into, if you’ve laid the proper groundwork for your story, the solution will arise from material you’ve already planted. So go ahead and gloss over these details in your selling synopsis, but be assured when you come to them in the story, the muse will help you fill in those plot holes. You can rewrite your synopsis accordingly.
So who else has backed a character into a corner, and how did you get him out?