While researching an unrelated topic last year, I found a cool tidbit and tucked it away (as I often do) to use in a story someday. Since I doubt I ever will, perhaps one of you can put this research to good use.
First, a question.
What do you think is a forensic investigator’s worst nightmare?
Did anyone guess a cute ’n cuddly koala? No? I didn’t think so. In all fairness, I would never have guessed it either, but the koala could keep investigators on their toes. I’ll tell you why in a minute.
Apes & Chimpanzees
As children, we’re taught apes and chimpanzees are our closest living relatives. The similarities are obvious. No one can stare into the eyes of these gentle beings and deny their humanity. Both animals also have astonishing intelligence.
Remember Koko?
Koko, the western lowland gorilla that died in her sleep in 2018 at age 46, stunned researchers with her emotional depth and ability to communicate in sign language. She garnered international celebrity status with her vocabulary of more than 1,000 signs and the ability to understand 2,000 words of spoken English.
National Geographic magazine featured Koko on its cover twice. First in October 1978, with a selfie Koko snapped in a mirror. Then in January 1985, when National Geographic ran a story about Koko and her pet kitten.
“Because she was smart enough to comprehend and use aspects of our language, Koko could show us what all great apes are capable of: reasoning about their world, and loving and grieving the other beings to whom they become attached,” Barbara King, a professor emerita of anthropology at the College of William and Mary
In addition to language, Koko’s behavior revealed human emotions. She also seemed to have a sense of humor, and even a bit of playful mischievousness, as portrayed in this video of Koko and Robin Williams.
There’s no denying the human qualities of apes and chimps. But did you know a koala’s fingerprints are so similar to humans the Australian police once feared they’d cause confusion at crime scenes? It’s true.
Similar confusion occurred in the UK during a time when unsolved crime was at an all-time high. In fact, in 1975, British police raided the ape houses at London and Twycross Zoos. According to The Independent, the police targeted “Half a dozen chimpanzees and a pair of orangutans.”
The objective was to fingerprint these animals, partly because the UK police referred to smudged or unclear fingerprints as “monkey prints.”
“If you passed a chimpanzee print to a fingerprint office and said it came from the scene of a crime, they would not know it was not human.” Steve Haylock, City of London Police fingerprint bureau
The chimpanzees and orangutans didn’t mind being fingerprinted. If you’re curious, none of the prints led to solving the string of unsolved crimes. All the furry suspects appeared to be upstanding members of society. 😉
Meanwhile, in Australia…
Police feared koalas may have contaminated a criminal investigation. Why? Because like apes and chimpanzees, koalas possess freakishly human fingerprints. The deltas, loops, and whirl patterns of a koala’s fingerprint are as individual as our own. Yet most tree-dwelling mammals don’t possess humanlike prints.
“It appears that no one has bothered to study them in detail,” said Macie Henneberg, forensic scientist and biological anthropologist at the University of Adelaide, Australia. “Although it is extremely unlikely that koala prints would be found at the scene of a crime, police should at least be aware of the possibility.”
Some researchers believe that even after closely inspecting the fingerprints under a microscope, investigators would not be able to distinguish a human print from fingerprints left by a koala. Even their closest relatives—kangaroos and wombats—don’t possess fingerprints. The weird part is Koala prints seemed to have evolved independently, and much more recent than primates.
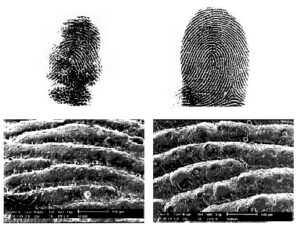
Can you guess which print is human?
Click the image to enlarge.
Top row: Standard ink fingerprints of an adult male koala (left) and adult male human (right).
Bottom row: Scanning electron microscope images of epidermis covering fingertips of the same koala (left) and the same human (right).
What do humans, apes, chimps, and koalas have in common?
The need to grasp. Yes, it could be that simple.
Researchers at the University of Adelaide discovered koala prints in 1996 and wrote a paper on their findings:
“Koalas … feed by climbing vertically onto the smaller branches of eucalyptus trees, reaching out, grasping handfuls of leaves and bringing them to the mouth… These forces must be precisely felt for fine control of movement and static pressures and hence require orderly organization of the skin surface.”
Makes sense, right?
But wait—there’s more!
I discovered one other fascinating tidbit about fingerprints that I never knew.
Genetics form the base of a fingerprint, but they are personalized when the baby touches the inside of their mother’s womb, resulting in unique whirls, deltas, and loops. Hence why identical twins don’t share identical fingerprints. Each baby touched the womb wall in his or her own unique way, swirling and drawing like finger paints on a bathtub wall.
Maybe it’s me—I do tend to get overly sentimental around holidays—but I find it heartwarming to think the tips of our fingers forever preserve the unbreakable bond between momma and baby, imprinted for eternity.
I hope my discoveries kickstart your creativity in new and unsuspecting ways. Happy Labor Day to our U.S. readers! May your burgers be sizzlin’, the buns toasted to perfection, and your beverages be cold. 😀