by James Scott Bell
@jamesscottbell
 I love this place.
I love this place.
Remember when sepia-tone Dorothy opens the door of her transported house, and sees a strange world of vivid colors, striking flora, and giggling Munchkins? We are not in Kansas anymore!*
What adventures await? What discoveries? And dangers! Good witches and bad witches, trees that throw their fruit, lions, tigers and bears. Oh my!
Well, that’s how I feel at the beginning of a project. I’m in a land of infinite possibilities and not wedded to any of them. I get to explore. I take a stroll down a yellow-brick road and come to a fork. “Some people do go both ways,” a friendly scarecrow tells me. Off I go one way, taking notes. I decide to go back and take another way. Takes me a millisecond to get to another setting entirely. More notes and ideas for plot, characters, twists, turns and settings.
I call this my “white hot document.” I’m recording what ifs and what nows as fast as they come to me. I don’t settle on one direction just yet.
The next day I come back for more. I annotate the notes, highlighting what still excites me, and go off again. I add more characters, scene ideas, plot possibilities. Lather, rinse, repeat.
After a week or so the story I really want to tell—or, more accurately, the story that wants me to tell it—begins to take shape.
This is the most enjoyable part of writing for me. The world is my oyster and there are pearls all around.
Now the work begins. I start to lay out my scene cards (in Scrivener), concentrating on my signpost scenes. Especially my Mirror Moment, which becomes the beam of light that helps me navigate the story from opening Disturbance, through the Doorway of No Return, to the final Transformation. I’m still having fun.
Then comes the writing, which sometimes flows (lots of fun), sometimes slogs (ack). But either way, I make sure the word quota gets done. There’s always satisfaction in that.
Finally, I get to the end. I work on this part the most, the last fifty pages. I know I’ve hit the mark when emotions kick in. Elation, deep satisfaction, sometimes laughter, sometimes tears.
Yes, I’ll admit it. I have on more than one occasion experienced the waterworks when I hit just the right note of resonance. Like when I typed the last line of Try Fear. It was the end of my Ty Buchanan legal thriller trilogy. I’ve had a consistent stream of emails asking me to continue this series, but I am loath to mess with what I consider my most perfect ending.
I set the first draft aside for a few weeks.
Then comes the first read-through, in hard copy. I don’t particularly enjoy this part, but know it’s make things better. I make my revisions, then give it to my first reader, the sainted Mrs. B.
This is the hard part! Waiting for her notes, then going through the book with her page by page. It’s like surgery. Nobody chooses surgery as a fun activity, but you take it when you know it will make you healthier. Ditto your book.
And then you’re in recovery which is, for me, the final polish. The last tinkering, usually with dialogue and scene endings.
Proof reader next. Then, finally, out the book goes to the world. This is really enjoyable as an indie, because I don’t have to wait a year for the book to hit the shelves. Thus, launch day is champagne day. I pop a bottle for my wife and me, and usually cook up a rib-eye on the barbie, to be enjoyed with a nice cabernet.
I awaken the next day, and open the door to a new world of vivid colors…
What’s your favorite part of the writing process? The least favorite? How do you treat yourself when your book is finally published?
*Bonus Note: How did The Wizard of Oz pull off the effect of Dorothy opening the door in B&W to reveal a Technicolor world? It was ingenious for the day. The entire scene was shot in color! The interior of the house was painted in sepia tones, and “Dorothy” was really Judy Garland’s stand-in, in a sepia dress, black wig, and dark makeup on the arms. Notice that she pulls the door open, revealing the colorful world, and backs out of the shot. That’s when Judy Garland moves into the scene, carrying a fake Toto. Watch:

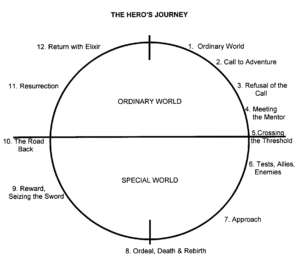




 The prime example of Bitter Experience is Casablanca. Rick Blaine had his heart shattered when the woman he loved, Ilsa Lund, abandoned him in Paris just before the Nazi occupation. He has set up shop in Casablanca to forget her. His café is allowed to operate because he takes no sides in the war. His Call to Adventure comes when Ugarte, the scheming rat who murdered German couriers to obtain the valuable Letters of Transit, begs Rick to hide him from the police. Rick refuses with the classic line, “I stick my neck out for nobody.”
The prime example of Bitter Experience is Casablanca. Rick Blaine had his heart shattered when the woman he loved, Ilsa Lund, abandoned him in Paris just before the Nazi occupation. He has set up shop in Casablanca to forget her. His café is allowed to operate because he takes no sides in the war. His Call to Adventure comes when Ugarte, the scheming rat who murdered German couriers to obtain the valuable Letters of Transit, begs Rick to hide him from the police. Rick refuses with the classic line, “I stick my neck out for nobody.” A refusal out of fear or self-doubt must be overcome with a strong emotional jolt. In Finding Nemo, Marlin, Nemo’s father, is afraid of the open ocean because of a past traumatic event—a barracuda attack that killed his wife, Cora, and most of their eggs. He is therefore overprotective of his surviving son, Nemo. Nemo keeps calling his father to adventure—exploring the sea, finding a sea turtle, etc. But Marlin refuses. He is full of fear and self-doubt about his ability to protect his son.
A refusal out of fear or self-doubt must be overcome with a strong emotional jolt. In Finding Nemo, Marlin, Nemo’s father, is afraid of the open ocean because of a past traumatic event—a barracuda attack that killed his wife, Cora, and most of their eggs. He is therefore overprotective of his surviving son, Nemo. Nemo keeps calling his father to adventure—exploring the sea, finding a sea turtle, etc. But Marlin refuses. He is full of fear and self-doubt about his ability to protect his son.