How Right Do Your Characters Have to Be?
Or, who are you going to upset or offend with this book?
Terry Odell
 Clichés are to be avoided, they tell us. So are stereotypes. (Still haven’t figured out who “they” is, but my grandfather apparently knew them well, as they were always making mistakes he’d get blamed for.)
Clichés are to be avoided, they tell us. So are stereotypes. (Still haven’t figured out who “they” is, but my grandfather apparently knew them well, as they were always making mistakes he’d get blamed for.)
But a cliché can provide a shortcut to understanding or visualizing a scene, and a stereotype might offer a shortcut to getting a handle on a character. Nothing is all good or all bad.
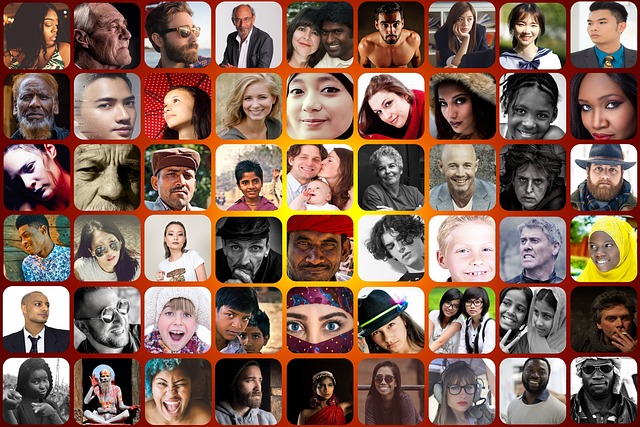
Publishers are looking for diversity these days. I’m going out on a limb here and saying very few of us belong to more than a small number of different ‘groups.’ Gender, ethnicity, religion, age. If we want diversity in our books, we’re going to be writing about people different from ourselves.
How do we get it “right?” Is there even a “right?” Can we say all golden retrievers are happy, people-loving dogs? Are all Staffordshire terriers dangerous? Same goes for people. Yet we categorize and generalize.
Years and years ago, my mom became good friends with our next-door neighbor. The two of them went to the beach one day, and the neighbor found out my mom was Jewish. She was surprised—maybe even shocked. Her words: “I’d never have thought you were Jewish. You’re so nice.” The neighbor wasn’t from Los Angeles, where we lived, and her exposure to diversity was obviously limited. Her perceptions were ruled by her experience. I still wonder if she and my mom would have been friends had the neighbor known at their first meeting that my mom was Jewish.
In my Mapleton books, Sam and Rose Kretzer are Jewish, and I’m sure many people think some of their behaviors are wrong. They’re bringing their own perceptions and experiences, and making generalizations. Rose is a conglomerate of many of my relatives. Trying to get a Jewish character right is next to impossible, one simple reason being there are so many different sects or denominations, and there’s diversity within each.
 Today, there are warnings about getting diverse characters right to the point that some authors are hiring sensitivity readers, or at least running pertinent sections by members of whatever group their character belongs to. I have a trans character in one of my Mapleton books, and I approached a trans author to make sure I got it right. Was it right for everyone? I don’t know. I haven’t seen any negative comments, so maybe I did. Also, the character was a minor one, and didn’t have a lot of page time.
Today, there are warnings about getting diverse characters right to the point that some authors are hiring sensitivity readers, or at least running pertinent sections by members of whatever group their character belongs to. I have a trans character in one of my Mapleton books, and I approached a trans author to make sure I got it right. Was it right for everyone? I don’t know. I haven’t seen any negative comments, so maybe I did. Also, the character was a minor one, and didn’t have a lot of page time.
I do know that after my first few books, which were (and still are because I’m not updating them) populated predominantly by white cis characters, I began including more diversity. Would I ever try a protagonist who’s substantially different from me? Other than writing males, I don’t think so. There’s too much to get wrong, and too many people who are offended by mistakes.
 Something as simple as age is another thing to try to get right (which is what sparked the idea for this post).
Something as simple as age is another thing to try to get right (which is what sparked the idea for this post).
I get the New York Times’ daily digest in my email, and a headline saying It’s Fun to Be Alive’: 13 Older Photographers Show Us Their Work — and Themselves piqued my interest, so I opened it. Older, eh? I’m older than most of them. I’m not pretending to be any age other than mine, but it’s being put into a box that’s the problem.
A while back, I agreed to read a chapter that was giving an author acquaintance trouble. He’d included a secondary character who I’m sure was meant to be a mood-lightener. Stereotypical elderly woman. Hairnet, orthopedic shoes, walking stick, thick glasses—the works. Her age? 65. I came down fairly hard on the author for that one. I’m ten-plus years older than that character, and that kind of a stereotype bugs the heck out of me.
That, for me, is what we as authors need to consider when we’re creating and describing any character, be it their age, gender, ethnicity, religion, dietary habits—the list is endless. And these days, people are eager to jump down your throat if your description deviates in the slightest from their perception.
What about you, TKZers? How do you get things right for your characters? Or don’t you care how readers will perceive them because you’ll never please everyone?
 Available Now
Available Now
Deadly Relations.
Nothing Ever Happens in Mapleton … Until it Does
Gordon Hepler, Mapleton, Colorado’s Police Chief, is called away from a quiet Sunday with his wife to an emergency situation at the home he’s planning to sell. A man has chained himself to the front porch, threatening to set off an explosive.
 Terry Odell is an award-winning author of Mystery and Romantic Suspense, although she prefers to think of them all as “Mysteries with Relationships.”
Terry Odell is an award-winning author of Mystery and Romantic Suspense, although she prefers to think of them all as “Mysteries with Relationships.”

 Garry Rodgers is a retired homicide detective with a second career as a coroner—pretty much Doctor Death for over thirty years. Now, Garry is a caped crime writer who fights villainous words rather than crafty crooks and deadly stiffs.
Garry Rodgers is a retired homicide detective with a second career as a coroner—pretty much Doctor Death for over thirty years. Now, Garry is a caped crime writer who fights villainous words rather than crafty crooks and deadly stiffs.